EV Battery Recycling: Step-by-Step Process
Mia Wilson
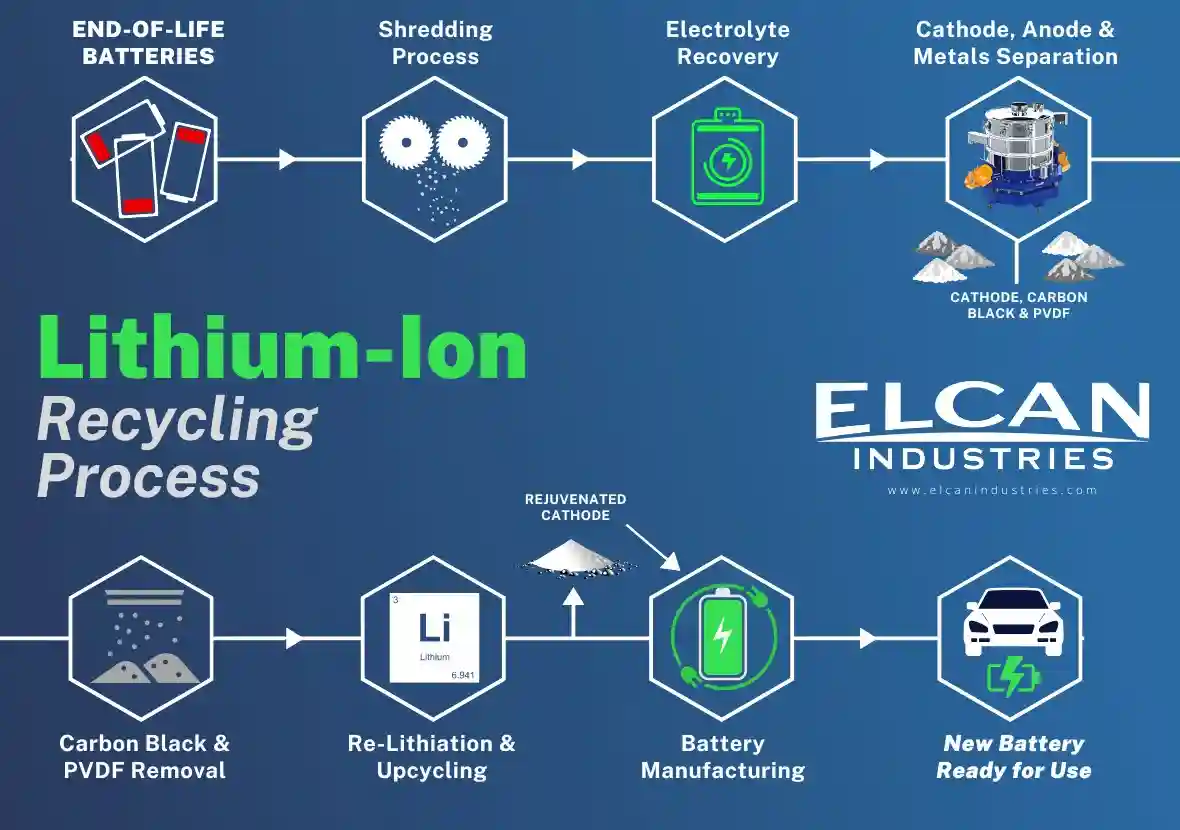
Photo: EV Battery Recycling: Step-by-Step Process
EV Battery Recycling: Step-by-Step Process
Introduction
Electric vehicles (EVs) have emerged as a crucial solution to reduce greenhouse gas emissions and combat climate change. However, as EV adoption rises globally, the demand for lithium-ion batteries critical components in EVs also surges. While EV batteries have a lifespan of 8 to 15 years, they eventually degrade, leading to a critical question: what happens to these batteries when they reach the end of their life cycle? This is where EV battery recycling becomes essential. Proper recycling not only prevents environmental damage but also recovers valuable materials. This article delves into the step-by-step process of EV battery recycling, shedding light on its importance, techniques, and future prospects.
Why EV Battery Recycling Matters
Before diving into the process, it’s important to understand the significance of EV battery recycling. A typical EV battery contains materials such as lithium, cobalt, nickel, and manganese, which are finite resources. If discarded improperly, these batteries can pose environmental risks, including groundwater contamination and toxic waste buildup. Recycling helps:
- Conserve natural resources by recovering metals.
- Reduce environmental impact by preventing toxic leakage.
- Lower the cost of EV production by reusing scarce materials.
- Minimize reliance on mining, which often causes ecological degradation.
Step-by-Step Process of EV Battery Recycling
1. Collection and Transportation
The first step in the recycling process is collecting used EV batteries. Collection systems are set up by manufacturers, recycling companies, or authorized waste disposal centers. Once collected, the batteries are transported to recycling facilities in compliance with strict safety regulations to prevent accidents such as short circuits, leaks, or fires.
Key Considerations During Collection:
- Safety protocols must be followed to handle potentially hazardous batteries.
- Batteries are stored in fireproof containers during transportation.
- Facilities are equipped with monitoring systems to detect any signs of damage or overheating.
2. Discharging the Battery
Before dismantling, the battery must be fully discharged to prevent accidental electrocution or short circuits during handling. Specialized equipment is used to safely drain the remaining energy. In some cases, partially discharged batteries can be repurposed for second-life applications, such as energy storage systems.
3. Dismantling and Sorting
Once discharged, the battery is dismantled to separate its various components. EV batteries consist of modules, which in turn are made up of individual cells. These cells are encased in protective housing, which must be carefully removed. After dismantling, the components are sorted into:
- Cathode materials (lithium, cobalt, nickel)
- Anode materials (graphite)
- Electrolytes
- Metal casings and wiring
This step is labor-intensive and requires precision to avoid damaging reusable materials.
4. Shredding and Crushing
The sorted components are then sent through shredding machines. Shredding breaks down the battery into smaller pieces, making it easier to extract valuable metals. After shredding, the crushed material is further processed to separate metals from plastics and other non-metallic components.
5. Hydrometallurgical and Pyrometallurgical Processes
The shredded material undergoes either a hydrometallurgical or pyrometallurgical process or a combination of both to recover key materials.
- Hydrometallurgy: Involves the use of chemical solutions to leach valuable metals such as lithium, cobalt, and nickel from the shredded material. This process is efficient, environmentally friendly, and yields high-purity materials.
- Pyrometallurgy: Involves heating the material at high temperatures to melt and separate metals. While effective, it consumes more energy and produces emissions.
Both processes aim to recover critical metals that can be reused in the production of new EV batteries.
6. Refining and Purification
After extraction, the recovered metals undergo refining and purification to meet the quality standards required for battery manufacturing. High-purity metals are essential to ensure the performance and longevity of new EV batteries. This stage may involve additional chemical treatments and filtration processes.
7. Repurposing or Reuse of Materials
Finally, the purified materials are either sold to battery manufacturers or reused directly in the production of new batteries. In some cases, components such as casings and electrodes are repurposed for industrial applications. This closed-loop recycling approach ensures a sustainable supply chain and reduces the overall carbon footprint of EV production.
Challenges in EV Battery Recycling
While EV battery recycling holds immense potential, it also faces significant challenges:
- High cost of recycling: The process involves advanced technology and labor, making it expensive.
- Complex battery designs: Different manufacturers use varying designs, which complicates the dismantling and sorting process.
- Limited infrastructure: Many regions lack sufficient recycling facilities and collection networks.
- Environmental concerns: Although recycling reduces waste, certain steps especially pyrometallurgy can have an environmental impact if not properly managed.
Efforts are underway to overcome these challenges. For instance, some companies are investing in automated dismantling systems to reduce labor costs, while governments are offering incentives to encourage recycling initiatives.
The Future of EV Battery Recycling
The future of EV battery recycling looks promising, driven by increasing regulatory pressure and technological advancements. Governments across the world are introducing policies to promote battery recycling. For example, the European Union has mandated that by 2030, 70% of EV batteries must be recycled.
Moreover, research is focused on developing more efficient recycling methods, such as direct recycling, which aims to recover materials without breaking them down chemically. Innovations in second-life applications are also gaining traction, with used EV batteries being repurposed for renewable energy storage.
Conclusion
EV battery recycling is not just a technological necessity it’s an environmental imperative. By following a well-defined step-by-step process, valuable materials can be recovered, waste can be minimized, and the overall sustainability of electric vehicles can be improved. However, significant challenges remain, and continued efforts from governments, manufacturers, and researchers are needed to make EV battery recycling more efficient and widespread.
As the world transitions towards a greener future, investing in and supporting EV battery recycling will play a critical role in ensuring that the environmental benefits of electric vehicles are fully realized.
For You
View AllLearn how VPS hosting boosts website performance and speeds up loading times.
Mia Wilson
Upgrade your off-road truck with the best mods for performance and durability. Discover top picks for your adventure today!
Mia Wilson
Discover the top 10 adventure destinations around the world. From hiking to diving, find your next thrilling escape today!
Mia Wilson
Compare run-flat tires with normal tires to see their pros, cons, and which is better for your driving needs. Learn more today!
Mia Wilson
Unlock the health benefits of adequate sleep and boost your well-being. Learn why sleep is essential for your health. Click to read more!
Mia Wilson
Uncover the fascinating story of who invented the first car and how it revolutionized transportation. Dive into automotive history!
Mia Wilson
Health








Education
View All
April 19, 2025
What Is Educational Psychology?
Discover educational psychology and how it enhances teaching and learning processes. Unlock better understanding today!

May 27, 2025
What Is Brown vs. Board of Education?
Explore the historic Brown vs. Board of Education case, its impact on civil rights, and its legacy. Learn why it matters today!
May 3, 2025
What Is Bilingual Education?
Explore bilingual education, its benefits, and how it fosters cultural understanding and cognitive growth. Learn more!