Income Tax vs. Wealth Tax: Key Differences
Mia Wilson
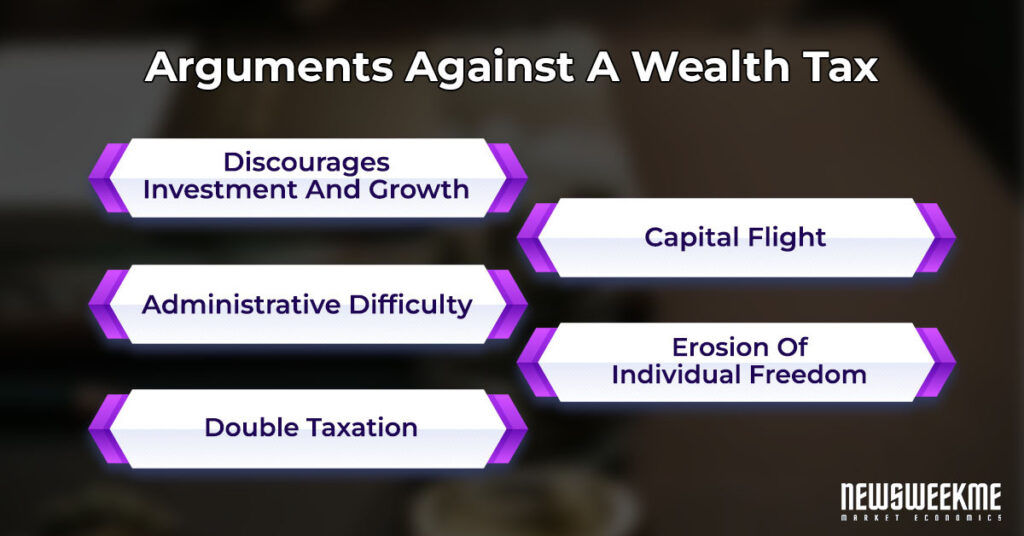
Photo: Income Tax vs. Wealth Tax: Key Differences
Income Tax vs. Wealth Tax: Key Differences
Taxation forms an integral part of any economy, serving as the primary means through which governments generate revenue to fund public services and infrastructure. While most people are familiar with income tax, fewer understand the concept and purpose of wealth tax. These two types of taxes have distinct structures, objectives, and implications for taxpayers. This article explores the key differences between income tax and wealth tax, shedding light on their unique characteristics, roles in economic policy, and effects on individuals and businesses.
Introduction to Income Tax and Wealth Tax
What is Income Tax?
Income tax is a direct tax levied on an individual's or entity's income. In most countries, income tax applies to various sources of income, including wages, business profits, investments, and rental earnings. Governments typically collect income tax at progressive rates, meaning higher-income earners pay a larger percentage of their earnings in tax. Income tax serves as a major revenue source and plays a critical role in funding government operations and social programs.
What is Wealth Tax?
In contrast, wealth tax is a levy on the net worth of an individual or entity. Unlike income tax, which focuses on yearly earnings, wealth tax targets the cumulative value of assets owned, including real estate, stocks, bank balances, and luxury possessions. While less common than income tax, wealth tax is implemented in certain countries to reduce wealth inequality and ensure that high-net-worth individuals contribute proportionately to public finances.
Key Differences Between Income Tax and Wealth Tax
1. Basis of Taxation
The primary distinction between income tax and wealth tax lies in their respective bases of taxation.
- Income Tax: Imposed on earned and unearned income over a specific period, typically a fiscal year. It affects wages, salaries, interest, dividends, and business profits.
- Wealth Tax: Applied to the total value of assets owned by an individual or entity, minus any liabilities. This makes it a tax on accumulated wealth rather than yearly earnings.
2. Tax Rates and Calculation
- Income Tax Rates: Most countries adopt a progressive income tax system, meaning that the tax rate increases as the income level rises. Different income brackets are subject to varying rates, with exemptions and deductions helping to lower taxable income.
- Wealth Tax Rates: Wealth tax rates tend to be lower, often ranging from 0.1% to 2% of total net worth. However, because wealth is accumulated over time, even a small percentage can represent a significant amount.
3. Purpose and Economic Impact
- Income Tax Objective: The primary goal of income tax is to generate revenue for government spending. Additionally, progressive income tax systems aim to promote social equity by ensuring that higher earners contribute a larger share.
- Wealth Tax Objective: Wealth tax is often introduced to address wealth concentration and inequality. By taxing accumulated wealth, governments aim to redistribute wealth more fairly and reduce the disparity between the rich and the poor.
4. Compliance and Administration
- Income Tax Compliance: Income tax requires individuals and businesses to file annual returns, declaring all sources of income. Governments may conduct audits to ensure compliance and prevent evasion.
- Wealth Tax Compliance: Calculating wealth tax involves assessing the market value of all owned assets, which can be complex. Ensuring compliance requires clear guidelines on valuation and reporting, making the administration of wealth tax more challenging.
5. Prevalence in Tax Systems Worldwide
- Income Tax: Nearly every country in the world has some form of income tax, making it a ubiquitous component of modern tax systems.
- Wealth Tax: Wealth tax is less common. While several European countries, including Spain, Norway, and Switzerland, levy wealth tax, many nations have abolished it due to difficulties in implementation and its potential to discourage investment.
Pros and Cons of Income Tax and Wealth Tax
Pros of Income Tax
- Broad Revenue Base: Since income tax is collected from a wide range of earners, it provides a steady and predictable revenue stream.
- Encourages Wealth Creation: Unlike wealth tax, income tax does not directly penalize wealth accumulation, fostering an environment conducive to investment and growth.
Cons of Income Tax
- Complexity: Progressive systems with multiple brackets and deductions can be confusing and prone to loopholes.
- Potential Disincentive to Work: High marginal tax rates may discourage individuals from increasing their income through additional work or investments.
Pros of Wealth Tax
- Reduces Inequality: Wealth tax targets individuals with high net worth, promoting a fairer distribution of wealth.
- Encourages Asset Utilization: By taxing idle wealth, it may motivate asset owners to invest or put their resources to productive use.
Cons of Wealth Tax
- Difficult Valuation: Accurately assessing the value of certain assets, such as real estate or privately held businesses, can be complex and subjective.
- Risk of Capital Flight: High-net-worth individuals may move their wealth to jurisdictions without wealth tax, reducing its effectiveness.
Income Tax and Wealth Tax in Practice
In practice, governments must balance revenue generation with economic growth and equity. While income tax remains the cornerstone of most tax systems, wealth tax is often viewed as a supplementary measure to curb excessive inequality. However, debates continue about the efficiency of wealth tax, with critics arguing that it can deter investment and entrepreneurship.
Conclusion
Both income tax and wealth tax serve distinct purposes in economic policy, addressing different aspects of financial equity and public revenue. While income tax focuses on annual earnings, wealth tax targets long-term wealth accumulation. Understanding their key differences helps taxpayers, policymakers, and businesses navigate the complexities of taxation.
Ultimately, the choice between relying more heavily on income tax or wealth tax depends on a country’s economic priorities, social policies, and administrative capabilities. Whether aiming to promote growth, reduce inequality, or fund essential services, governments must strike a careful balance to design a fair and effective tax system.
For You
View AllCompare synthetic fuel and diesel to understand their benefits, drawbacks, and environmental impact. Find the best option!
Mia Wilson
Discover actionable steps to start a small business and ensure its success. Click for expert tips and insights!
Mia Wilson
Learn what money supply is and how it influences inflation and economic growth. Click for key insights!
Mia Wilson
Discover effective strategies to protect your VPS from cyber threats.
Mia Wilson
Explore the steps to becoming a special education teacher and making a difference in students’ lives. Start today!
Mia Wilson
Understand macronutrients and micronutrients to optimize your diet. Learn the differences now!
Mia Wilson
Health










Education
View All
April 19, 2025
What Is Higher Education?
Understand higher education, its benefits, and how it shapes future opportunities. Explore your potential now!

April 18, 2025
What Is Special Education?
Dive into special education, its purpose, and how it supports students with unique needs. Learn how it changes lives!

April 30, 2025
How Important Is Technology in Education?
Explore how technology is revolutionizing education, enhancing learning, and creating future-ready skills. Learn more today!