Top Causes of Unemployment Explained
Mia Wilson
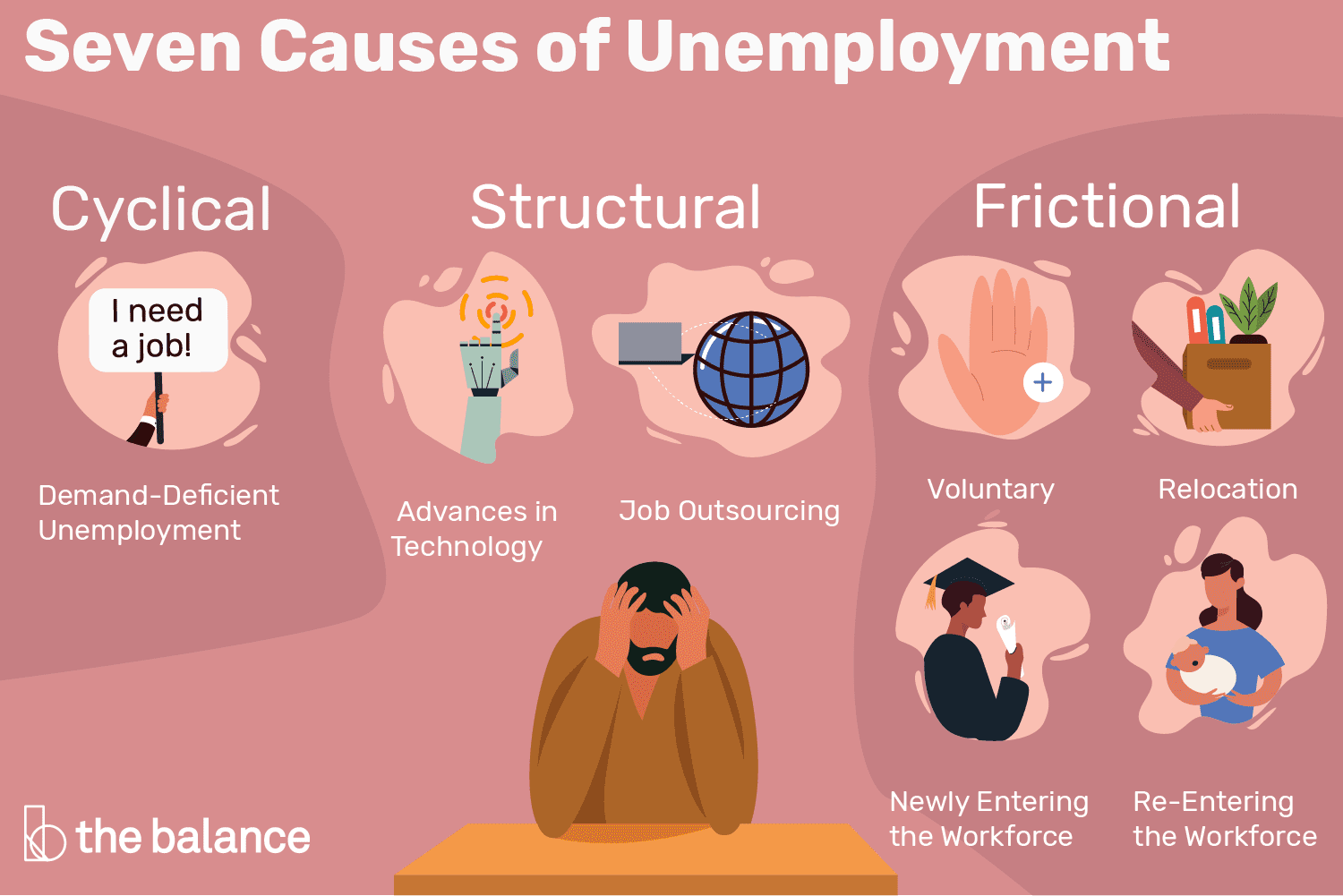
Photo: Top Causes of Unemployment Explained
Top Causes of Unemployment Explained: A Comprehensive Analysis
Unemployment is a critical economic issue that affects individuals, families, and entire nations. Despite economic advancements, many countries continue to struggle with unemployment. Understanding the primary causes is essential for policymakers, businesses, and job seekers to mitigate its effects. In this article, we’ll explore the top causes of unemployment, break down how they occur, and offer insights into potential solutions.
What Is Unemployment?
Before diving into the causes, it’s important to understand what unemployment means. Unemployment occurs when individuals who are capable and willing to work cannot find suitable jobs. The unemployment rate, a key economic indicator, measures the percentage of the labor force that is jobless but actively seeking employment.
Types of Unemployment
To better grasp its causes, it’s helpful to categorize unemployment into the following types:
- Frictional Unemployment – This occurs when individuals transition between jobs. It’s often short-term and part of a healthy economy.
- Structural Unemployment – This happens when there’s a mismatch between workers’ skills and job requirements.
- Cyclical Unemployment – This type is linked to the ups and downs of the economy. During a recession, cyclical unemployment tends to rise.
- Seasonal Unemployment – Caused by seasonal changes in labor demand, such as agricultural or holiday-related jobs.
- Technological Unemployment – Occurs when technological advancements render certain jobs obsolete.
Top Causes of Unemployment
Now that we’ve outlined the types, let’s examine the primary causes of unemployment in detail.
1. Economic Recession
Economic recessions lead to widespread job losses as businesses cut costs, including reducing their workforce. During a downturn, consumer spending decreases, causing businesses to experience lower demand. As revenues fall, many companies are forced to lay off employees to stay afloat. Cyclical unemployment typically spikes during recessions, impacting millions of workers.
Example: The global financial crisis of 2008 resulted in millions of job losses worldwide, with unemployment rates soaring in many developed countries.
2. Technological Advancements
While technology boosts productivity, it can also displace jobs, particularly those involving routine tasks. Automation, artificial intelligence, and robotics have replaced human labor in various industries, such as manufacturing and customer service. Workers who lack the skills to adapt to new technologies often find themselves unemployed.
Fact: A study by McKinsey Global Institute estimates that automation could displace up to 800 million jobs globally by 2030.
3. Structural Changes in the Economy
Structural unemployment arises when industries undergo significant changes. For instance, as economies shift from manufacturing-based to service-oriented models, workers with outdated skills may struggle to find new employment opportunities. Retraining and upskilling become crucial to address this issue.
Insight: The decline of coal mining jobs in many countries illustrates structural unemployment, as workers in that sector often face difficulties transitioning to other fields.
4. Globalization and Outsourcing
Globalization has led to the outsourcing of jobs to countries with lower labor costs. While this benefits businesses by reducing expenses, it often results in domestic job losses. Workers in developed countries, especially in manufacturing and customer support, are particularly affected by outsourcing.
5. Demographic Factors
Demographic shifts, such as an aging population or a sudden influx of young job seekers, can contribute to unemployment. In some cases, younger individuals may struggle to find work due to a lack of experience, while older workers may face age-related biases or skill gaps.
6. Education and Skill Mismatches
When education systems fail to equip individuals with the skills in demand by the labor market, structural unemployment increases. Employers may struggle to find qualified candidates even when job vacancies exist, leaving many workers unemployed despite their willingness to work.
Example: In rapidly evolving industries such as IT and healthcare, specific technical skills are in high demand, leaving many general degree holders unemployed.
7. Policy and Regulatory Factors
Certain government policies, such as high minimum wages or stringent labor regulations, can contribute to unemployment. While such policies aim to protect workers, they may also increase the cost of hiring, leading employers to reduce their workforce or turn to automation.
Debate: Economists often discuss the balance between labor protections and job creation. Striking the right balance is key to reducing unemployment without sacrificing workers' rights.
8. Natural Disasters and Pandemics
Natural disasters, such as earthquakes and hurricanes, disrupt local economies and lead to temporary or permanent job losses. Similarly, pandemics can have a severe impact on employment, as seen during the COVID-19 crisis when millions lost their jobs due to lockdowns and business closures.
Data: According to the International Labour Organization (ILO), global unemployment increased by over 33 million in 2020 due to the COVID-19 pandemic.
How Can Unemployment Be Reduced?
Addressing unemployment requires a multi-faceted approach involving governments, businesses, and individuals. Here are a few strategies:
- Investment in Education and Training: Ensuring that workers have the skills needed in a modern economy can reduce structural unemployment.
- Encouraging Entrepreneurship: Promoting small businesses and startups can create new jobs and stimulate economic growth.
- Active Labor Market Policies: Governments can implement job placement programs, offer wage subsidies, and invest in public works to reduce unemployment.
- Economic Stimulus Measures: During recessions, governments can introduce stimulus packages to boost demand and create jobs.
- Lifelong Learning Initiatives: Encouraging workers to continuously learn and adapt helps them stay relevant in a changing job market.
Conclusion
Unemployment is a complex issue with various causes, ranging from economic cycles to technological disruptions and globalization. Understanding the underlying factors is the first step toward finding effective solutions. By fostering skill development, encouraging innovation, and maintaining balanced policies, societies can work toward reducing unemployment and building a more resilient workforce.
Whether you’re a job seeker, policymaker, or business leader, staying informed about the causes of unemployment is crucial in navigating today’s dynamic job market. Tackling unemployment requires collective efforts and strategic actions to ensure that economic growth benefits all.
For You
View AllDiscover the ultimate luxury car brands that define sophistication, innovation, and performance. See the top picks now!
Mia Wilson
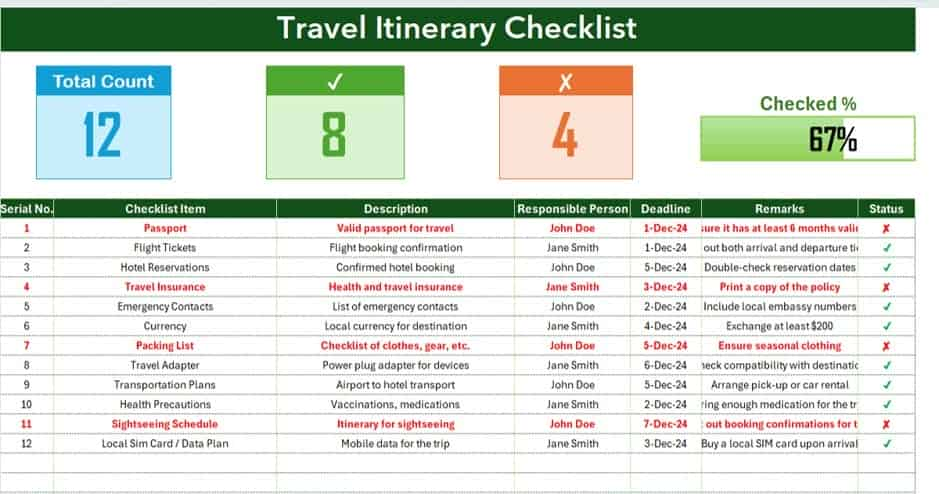
Never miss a detail with this travel itinerary checklist. Ensure your trips are smooth, organized, and unforgettable with these essential tips!
Mia Wilson
Get a beginner’s guide to cryptocurrency, its workings, and why it’s transforming finance. Click to stay informed!
Mia Wilson
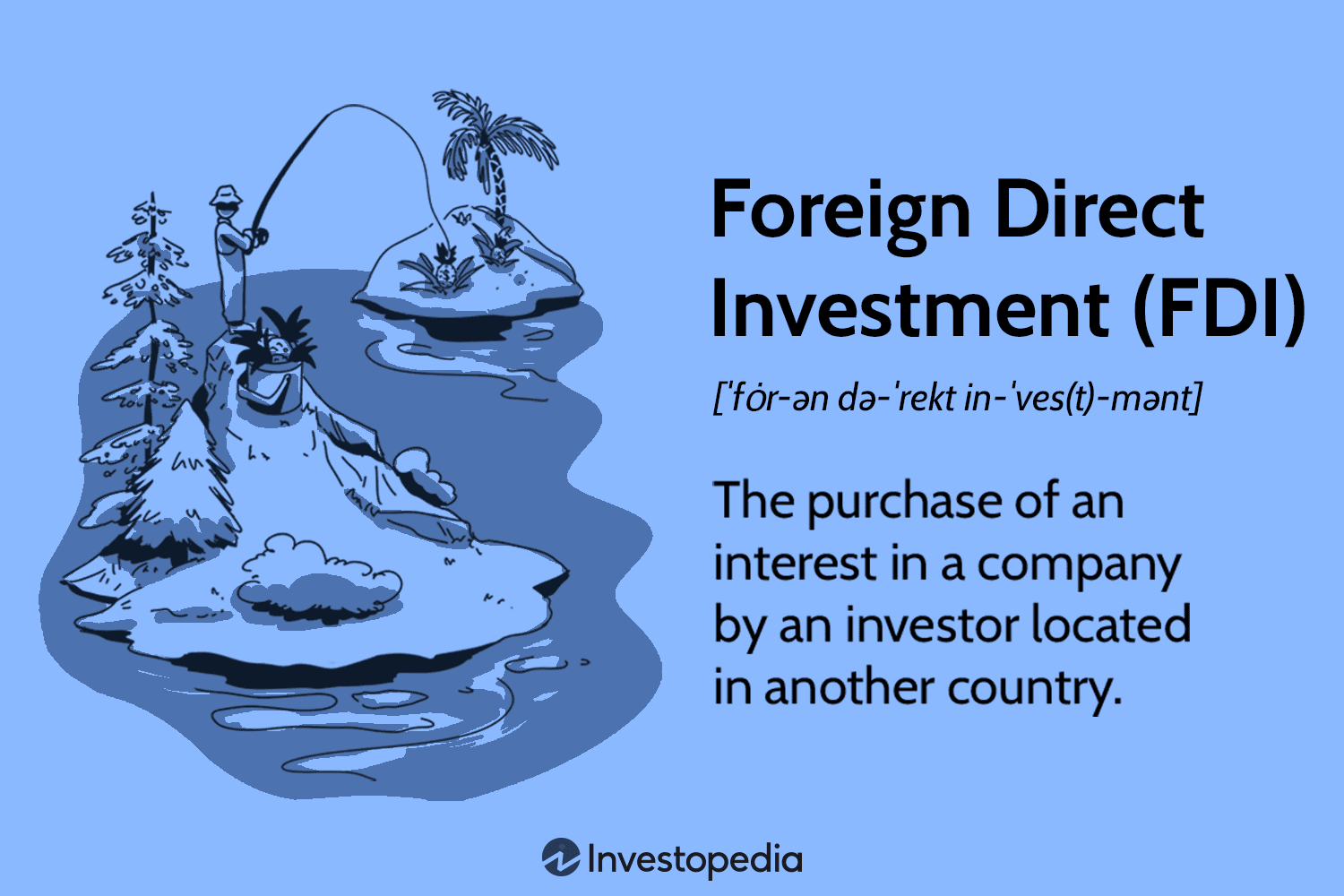
Understand Foreign Direct Investment (FDI), its benefits, and its role in global trade. Click for a comprehensive guide!
Mia Wilson
Learn about secondary education, its structure, and its role in shaping academic and career paths. Get insights today!
Mia Wilson
Uncover the meaning of venture capital, its benefits, and how it fuels startups. Click to understand its role in business!
Mia Wilson
Education
View All
April 22, 2025
What Is Early Childhood Education?
Explore early childhood education, its benefits, and how it shapes a child’s future. Start building strong foundations!

April 19, 2025
What Is Higher Education?
Understand higher education, its benefits, and how it shapes future opportunities. Explore your potential now!

April 18, 2025
What Is Special Education?
Dive into special education, its purpose, and how it supports students with unique needs. Learn how it changes lives!