Understanding Supply and Demand Basics
Mia Wilson
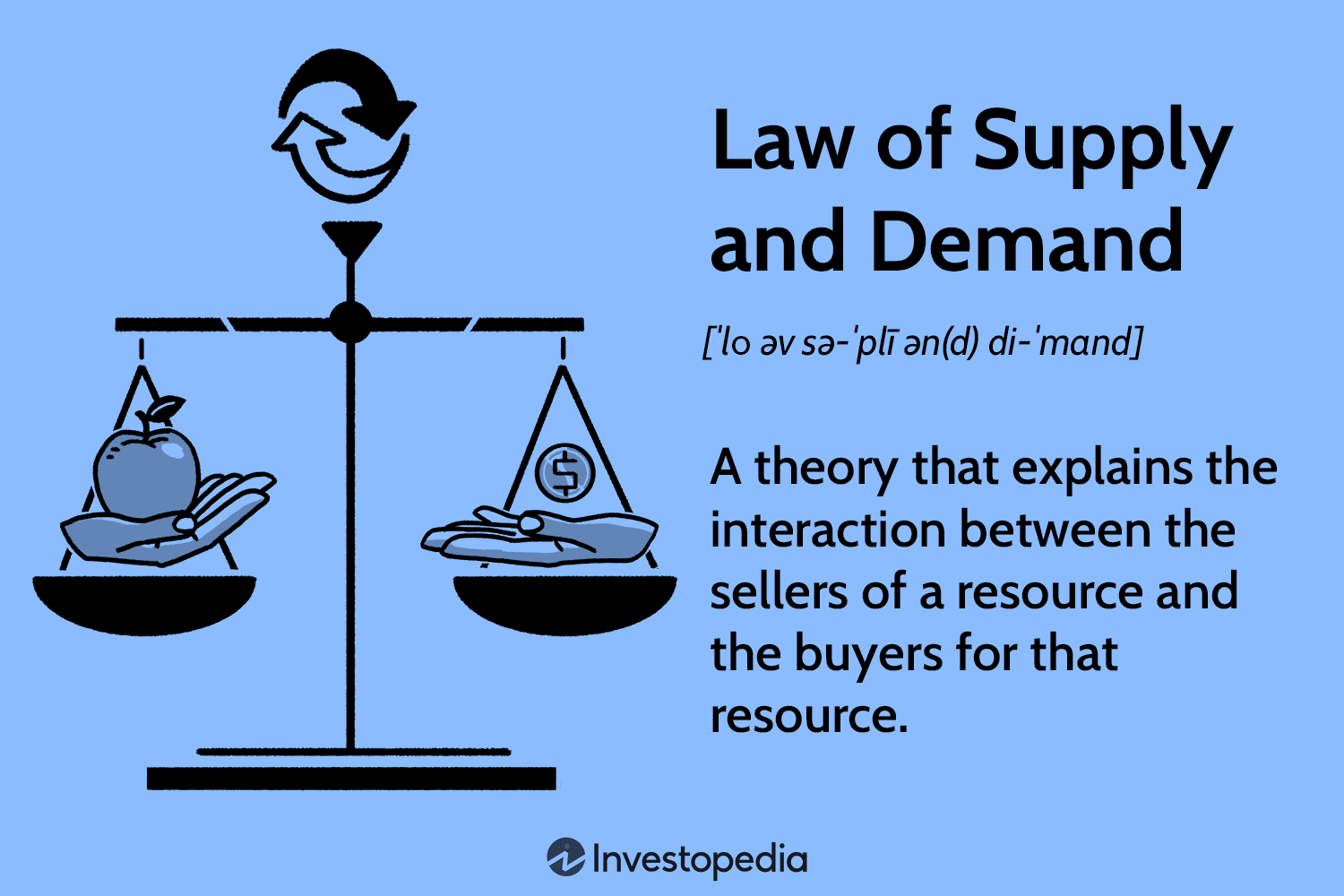
Photo: Understanding Supply and Demand Basics
Understanding Supply and Demand Basics: A Fundamental Guide for Everyone
Supply and demand are two of the most fundamental concepts in economics, driving the behaviors of markets, businesses, and consumers alike. Whether you're a budding economist, a business owner, or simply curious about how markets function, understanding supply and demand basics is crucial. This article provides an easy-to-understand explanation of these principles, delves into their importance, and offers real-world examples to help clarify how they shape the world around us.
Introduction: Why Supply and Demand Matter
At its core, economics revolves around the allocation of scarce resources, and supply and demand are central to this process. They form the foundation of market economies, influencing prices, production levels, and consumer behavior. Whether it’s determining the price of a gallon of gas or the availability of a new smartphone, the interaction of supply and demand governs these outcomes.
The interplay of supply (the quantity of goods producers are willing to sell) and demand (the quantity of goods consumers are willing to buy) dictates equilibrium a point where market forces balance. Without understanding these principles, it’s difficult to grasp how pricing works or why markets fluctuate.
Breaking Down the Basics: What Are Supply and Demand?
What Is Supply?
Supply refers to the quantity of a good or service that producers are willing to offer at various price points over a specific period. Several factors affect supply, including:
- Production Costs: Higher production costs may reduce supply since producing goods becomes less profitable.
- Technological Advancements: Innovations can improve efficiency, allowing producers to offer more at lower costs.
- Market Expectations: If producers expect future prices to rise, they may withhold supply temporarily, hoping to sell at a higher price later.
The Law of Supply
The law of supply states that, all else being equal, an increase in the price of a good leads to an increase in the quantity supplied. This relationship is depicted by an upward-sloping supply curve, highlighting that producers are generally more willing to produce and sell more goods at higher prices.
What Is Demand?
Demand represents the quantity of a good or service that consumers are willing to purchase at various price points over a period. Several factors influence demand:
- Consumer Income: Higher income typically increases demand as people can afford more goods.
- Tastes and Preferences: Changes in consumer preferences can shift demand patterns significantly.
- Prices of Related Goods: Substitutes and complements affect demand for example, a rise in the price of coffee might increase demand for tea.
The Law of Demand
According to the law of demand, when the price of a good rises, demand for that good generally decreases, assuming all other factors remain constant. This inverse relationship is illustrated by a downward-sloping demand curve.
The Concept of Market Equilibrium
Market equilibrium occurs where the supply and demand curves intersect. At this point, the quantity of goods supplied matches the quantity demanded, resulting in a stable market price. If the market price deviates from this equilibrium, it creates either a surplus or a shortage:
- Surplus: When supply exceeds demand, leading to downward pressure on prices.
- Shortage: When demand exceeds supply, causing prices to rise as consumers compete for limited goods.
Real-Life Example of Market Equilibrium
A classic example of equilibrium can be seen in the housing market. If too many houses are listed for sale at high prices but few buyers can afford them, prices tend to fall until they reach a level where buyers and sellers agree. Conversely, if housing supply is limited and demand remains high, prices increase until equilibrium is restored.
Shifts in Supply and Demand: What Causes Them?
While equilibrium represents a balance, real-world markets are rarely static. Shifts in supply and demand occur constantly, leading to changes in prices and quantities. Let’s explore what causes these shifts:
Factors Causing a Shift in Supply
- Changes in Input Costs: A rise in raw material costs can reduce supply, shifting the curve to the left.
- Natural Events: Droughts or other disasters can impact agricultural output, reducing supply.
- Government Policies: Taxes, subsidies, and regulations influence how much producers are willing or able to supply.
Factors Causing a Shift in Demand
- Economic Growth: As economies grow, consumers have more disposable income, increasing demand for goods and services.
- Demographic Changes: An aging population, for example, may increase demand for healthcare services.
- Marketing and Trends: Effective marketing campaigns can drive demand for specific products, even when prices remain constant.
Elasticity of Supply and Demand
Elasticity measures how sensitive supply or demand is to changes in price. A product is considered elastic if a small price change causes a significant change in quantity demanded or supplied. Conversely, it is inelastic if price changes have little effect on quantity.
Demand Elasticity Example
Luxury goods such as designer handbags tend to have high elasticity a slight price increase might lead to a large drop in demand as consumers switch to alternatives. On the other hand, essential goods like bread are usually inelastic because people need them regardless of price fluctuations.
The Importance of Supply and Demand in Business Strategy
Understanding supply and demand helps businesses make informed decisions about pricing, production, and inventory management. By analyzing demand trends, companies can anticipate shifts in consumer preferences and adjust their strategies accordingly. Similarly, monitoring supply conditions can help firms mitigate risks, such as rising input costs or supply chain disruptions.
Conclusion: Mastering Supply and Demand for Better Decisions
Grasping the basics of supply and demand is essential for anyone looking to understand how markets operate. Whether you're an investor, a business owner, or a curious consumer, knowing how supply and demand interact can improve decision-making and provide insights into market dynamics. From setting prices to predicting trends, the principles of supply and demand are a cornerstone of economic literacy.
For further reading, consider exploring introductory economics textbooks or attending online courses that delve deeper into these concepts.
For You
View AllFind out whether an SUV or a sedan is the better choice for your lifestyle. Compare space, performance, and efficiency now!
Mia Wilson
Discover the importance of health education in promoting wellness and preventing diseases. Start your journey to health today!
Mia Wilson
Get insights into VPS hosting prices and how to choose an affordable plan.
Mia Wilson
Save money while traveling with these 10 genius budget travel hacks. Explore the world without emptying your wallet!
Mia Wilson
Dive into special education, its purpose, and how it supports students with unique needs. Learn how it changes lives!
Mia Wilson
Learn why physical education is essential for health, academics, and personal growth. Get inspired to stay active!
Mia Wilson
Health







Education
View All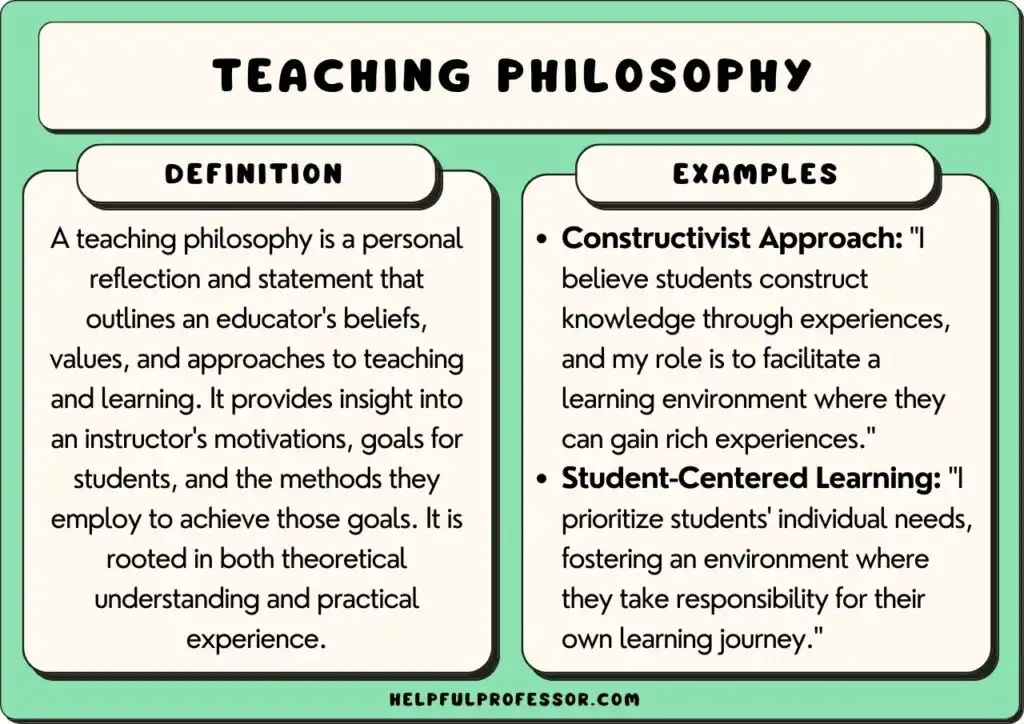
June 1, 2025
What Is Your Philosophy of Education?
Reflect on your philosophy of education, its core values, and how it influences teaching and learning practices. Discover your approach today!

April 14, 2025
What Is Physical Education? Explained!
Discover the importance of physical education, its benefits, and why it's crucial for overall development. Learn more now!

April 19, 2025
What Is Higher Education?
Understand higher education, its benefits, and how it shapes future opportunities. Explore your potential now!