What Is Your Philosophy of Education?
Mia Wilson
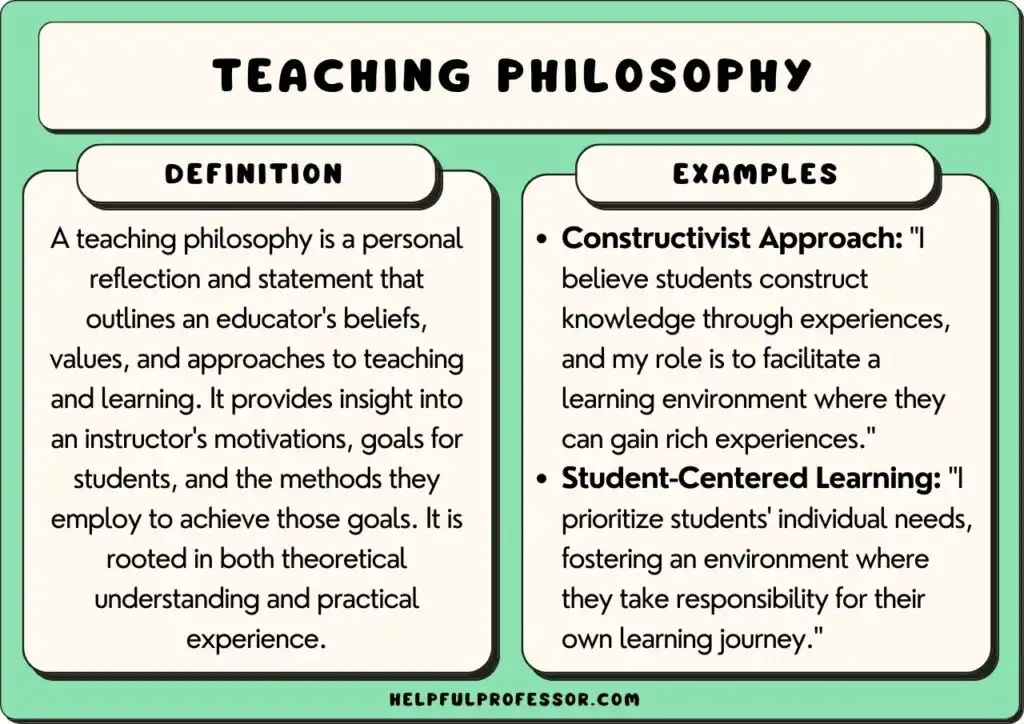
Photo: What Is Your Philosophy of Education?
What Is Your Philosophy of Education?
Education plays a foundational role in shaping individuals and society at large. However, the way we approach teaching and learning is deeply influenced by our personal and collective philosophies of education. A philosophy of education is more than just a set of beliefs about how people should learn it reflects values, goals, and methodologies that guide educators in their practice. This article explores the concept of educational philosophy, why it matters, and how various perspectives can shape both teaching styles and learning outcomes.
Understanding the Philosophy of Education
At its core, a philosophy of education encompasses an individual’s or institution’s beliefs about the purpose, process, and nature of education. It serves as a guiding framework for educators, helping them determine what knowledge is most important, how that knowledge should be delivered, and how students should engage with it.
Philosophies of education often address questions such as:
- What is the ultimate purpose of education?
- How do people learn best?
- What role do teachers play in the learning process?
- How should education prepare students for the future?
By answering these questions, educators can create a consistent approach to instruction that aligns with their values and beliefs.
Why a Personal Philosophy of Education Matters
Developing a personal philosophy of education is crucial for teachers, administrators, and even students. Here are some key reasons why it matters:
1. Clarifies Educational Goals
A clear philosophy helps educators define their primary objectives. For example, a teacher who believes in the transformative power of critical thinking may focus on fostering analytical skills in their students. On the other hand, an educator who values social responsibility might emphasize collaborative projects and community engagement.
2. Guides Teaching Methods
Different philosophies of education advocate different teaching strategies. A proponent of constructivism, for instance, may favor experiential learning, where students actively build knowledge through experience. In contrast, an educator who follows a more traditional approach might rely on direct instruction and rote learning.
3. Shapes Classroom Culture
An educator’s philosophy affects how they interact with students and establish classroom norms. A teacher who prioritizes student-centered learning will likely foster an environment where students feel empowered to voice their opinions, while a teacher with a more authoritarian style might emphasize discipline and structure.
Common Educational Philosophies
Educational philosophies have evolved over time, influenced by great thinkers and changing societal needs. Below are some of the most prominent philosophies:
1. Perennialism
Perennialism holds that education should focus on enduring ideas and universal truths. Proponents of this philosophy believe in teaching great works of literature, philosophy, and science that have stood the test of time. The goal is to cultivate rational thought and moral character.
Key Characteristics:
- Emphasis on classic texts and timeless knowledge.
- Structured, teacher-centered instruction.
- Development of intellectual and moral virtues.
2. Progressivism
Progressivism, championed by thinkers like John Dewey, emphasizes experiential learning and the development of critical thinking skills. This philosophy holds that education should be student-centered and relevant to real-world issues.
Key Characteristics:
- Focus on problem-solving and critical thinking.
- Hands-on, experiential learning.
- Encouragement of collaboration and social responsibility.
3. Essentialism
Essentialism advocates for a rigorous, standardized curriculum that focuses on core subjects such as reading, writing, math, and science. The philosophy aims to instill essential knowledge and skills that students need to succeed in life.
Key Characteristics:
- Teacher-centered instruction.
- Emphasis on mastery of fundamental subjects.
- Use of assessments to measure learning outcomes.
4. Constructivism
Constructivism posits that learners actively construct their own understanding of the world through experiences and reflection. This philosophy supports a more flexible approach to teaching, where students take an active role in their learning.
Key Characteristics:
- Student-centered learning.
- Emphasis on inquiry-based activities.
- Learning through exploration and discovery.
5. Humanism
Humanism focuses on the development of the whole person, emphasizing personal growth, self-actualization, and emotional well-being. Humanist educators prioritize creating a supportive learning environment that nurtures students’ individual potential.
Key Characteristics:
- Emphasis on self-directed learning.
- Nurturing a positive self-concept.
- Focus on students’ interests and emotional needs.
Creating Your Own Philosophy of Education
Whether you are an educator, a parent, or a student, developing your own philosophy of education can provide clarity and direction. Here are some steps to help you craft your philosophy:
1. Reflect on Your Educational Experiences
Think about your most memorable learning experiences. What made those experiences impactful? Were they driven by a passionate teacher, a hands-on project, or an inspiring subject? Identifying these moments can help you understand what you value in education.
2. Define Your Core Beliefs
Ask yourself fundamental questions about education. For instance:
- What do I believe is the primary purpose of education?
- How do I think students learn best?
- What role should teachers and students play in the learning process? Your answers to these questions will form the foundation of your philosophy.
3. Align Your Philosophy with Action
A philosophy of education is not just a theoretical framework it should influence your actions. Consider how your beliefs will shape your approach to teaching, curriculum design, and classroom management.
4. Be Open to Evolution
As you gain more experience in education, your philosophy may evolve. New experiences, research, and reflection can lead to a deeper understanding of what works best for you and your students.
The Impact of Educational Philosophy on Learning Outcomes
A well-defined philosophy of education doesn’t just benefit educators it has a direct impact on students’ learning outcomes. When teachers have a clear educational philosophy, they are more likely to create consistent and engaging learning experiences. This, in turn, fosters a positive learning environment where students can thrive.
For example, a teacher who believes in fostering creativity may integrate art and design into various subjects, helping students develop critical thinking and problem-solving skills. Conversely, an educator who values academic rigor might focus on high expectations and challenging coursework, leading to improved academic performance.
Conclusion
A philosophy of education is a powerful tool that shapes how we approach teaching and learning. Whether rooted in perennialism, progressivism, essentialism, constructivism, or humanism, each philosophy offers valuable insights into how education can be designed to meet the needs of learners. By reflecting on our own beliefs and values, we can develop a personal philosophy that not only guides our educational practices but also helps us contribute meaningfully to the broader educational landscape. Ultimately, understanding and articulating your philosophy of education can lead to more thoughtful, intentional, and impactful teaching and learning experiences.
For You
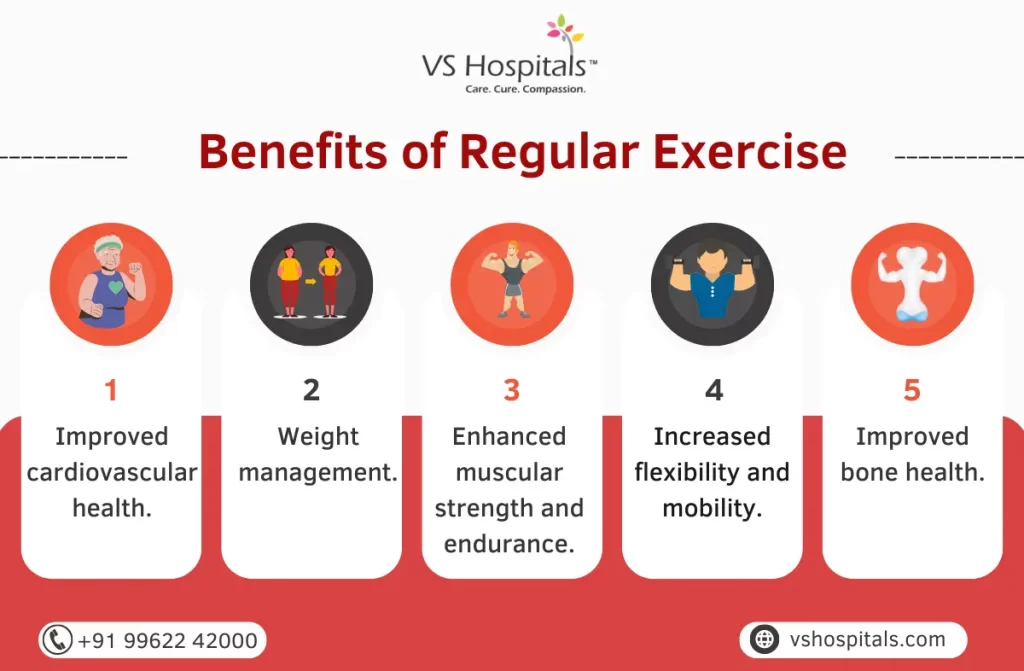
View AllDiscover the importance of physical education, its benefits, and why it's crucial for overall development. Learn more now!
Mia Wilson
Understand GDP growth and its role in measuring economic progress. Find out why it matters to everyone!
Mia Wilson
Discover how technology is transforming education, enhancing access, and reshaping classrooms. Explore its impact now!
Mia Wilson
Discover how crash tests are done and why they’re essential for vehicle safety. Explore the behind-the-scenes science now!
Mia Wilson
Understand post-secondary education, its types, and how it shapes careers. Start exploring your opportunities today!
Mia Wilson
Discover the best ways to showcase your education on a resume for maximum impact. Land your dream job now!
Mia Wilson
Education
View All
May 5, 2025
What Is General Education?
Learn what general education entails and its role in providing foundational knowledge for lifelong success. Start exploring today!
May 25, 2025
What Does Education Mean?
Unpack the meaning of education, its significance, and its role in transforming lives. Explore its essence today!

April 29, 2025
What Is Multicultural Education?
Dive into multicultural education and how it promotes diversity, inclusion, and equity in classrooms. Learn now!