What Is GDP Growth? Quick Guide
Mia Wilson

Photo: What Is GDP Growth? Quick Guide
What Is GDP Growth? Quick Guide
In today’s interconnected global economy, understanding key economic indicators is crucial for making informed financial, business, and policy decisions. One of the most significant indicators used to gauge a country’s economic health is Gross Domestic Product (GDP) growth. This quick guide will explore what GDP growth is, why it matters, how it’s measured, and its broader implications.
What Is GDP?
Before diving into GDP growth, it’s essential to grasp what Gross Domestic Product (GDP) represents. In simple terms, GDP refers to the total monetary value of all goods and services produced within a country’s borders over a specified period, usually a quarter or a year. It includes everything from agricultural products to manufactured goods and services like healthcare and entertainment.
GDP serves as a broad measure of a nation’s overall economic activity. Economists often use it to compare the economic performance of different countries or to assess changes in economic activity over time within a single nation.
Understanding GDP Growth
GDP growth refers to the increase in a country’s economic output over time. It is expressed as a percentage, showing how much the economy has expanded compared to the previous period. Positive GDP growth signals that the economy is growing, while negative growth, often referred to as a contraction, indicates a shrinking economy.
For example, if a country’s GDP in one quarter is $1.5 trillion and rises to $1.55 trillion in the next quarter, the GDP growth rate for that period would be approximately 3.3%.
How Is GDP Growth Measured?
Economists and governments rely on various methods to measure GDP growth. The two primary approaches are:
1. Nominal GDP vs. Real GDP
- Nominal GDP measures the value of goods and services at current market prices, without adjusting for inflation. This method can sometimes overstate growth if prices rise significantly.
- Real GDP, on the other hand, adjusts for inflation, providing a more accurate reflection of an economy’s true growth by using constant prices. Real GDP is generally preferred for measuring economic growth as it accounts for changes in purchasing power.
2. Annualized and Quarterly Growth Rates
GDP growth can be reported on a quarterly or annualized basis:
- Quarterly growth shows the percentage change in GDP from one quarter to the next.
- Annualized growth extrapolates quarterly growth to predict how much the economy would grow if the quarterly rate continued for a full year.
Why Is GDP Growth Important?
GDP growth is more than just a statistic it plays a pivotal role in shaping economic policy and influencing business and consumer decisions. Here’s why it matters:
1. Indicator of Economic Health
A growing GDP typically indicates a healthy economy, characterized by increasing production, job creation, and rising incomes. Policymakers use GDP growth as a gauge to determine whether the economy is expanding or contracting.
2. Influences Monetary and Fiscal Policy
Central banks, such as the Federal Reserve in the U.S., closely monitor GDP growth when setting interest rates. If growth is too fast, it can lead to inflation, prompting central banks to raise interest rates. Conversely, slow or negative growth may lead to lower interest rates to stimulate economic activity.
3. Impacts Investor Confidence
GDP growth can influence financial markets. Strong growth often boosts investor confidence, leading to increased investment in stocks and businesses. On the flip side, stagnant or negative growth can result in market volatility and decreased investment.
4. Standard of Living
Sustained GDP growth can lead to higher living standards as increased economic output often translates to more jobs, higher wages, and better public services. However, the distribution of economic benefits matters growth must be inclusive to improve the well-being of all citizens.
Factors Influencing GDP Growth
Several factors drive GDP growth. Understanding these drivers helps policymakers and businesses anticipate economic trends:
1. Consumer Spending
Consumer expenditure on goods and services is a major component of GDP. When households feel confident about their financial future, they tend to spend more, boosting economic growth.
2. Investment
Business investments in machinery, infrastructure, and technology contribute significantly to GDP growth. High investment levels often signal business confidence in future growth.
3. Government Spending
Public sector spending on infrastructure, education, and defense can stimulate economic activity, particularly during periods of slow private sector growth.
4. Net Exports
Exports add to a country’s GDP, while imports subtract from it. A trade surplus (more exports than imports) can enhance GDP growth, while a trade deficit can have the opposite effect.
5. Technological Advancements
Innovation and productivity improvements enable economies to produce more with the same or fewer inputs, driving long-term GDP growth.
GDP Growth vs. Other Economic Indicators
While GDP growth is a critical measure of economic performance, it should not be viewed in isolation. Other indicators, such as employment rates, inflation, and income inequality, provide a more comprehensive picture of economic well-being.
For example:
- Low unemployment alongside strong GDP growth signals a robust labor market.
- Rising inflation during periods of high GDP growth may indicate overheating, requiring policy intervention.
- Income inequality can persist even during high growth periods, highlighting the need for inclusive growth strategies.
Criticisms of GDP Growth as an Indicator
Despite its widespread use, GDP growth is not without its critics. Common criticisms include:
1. Ignores Environmental Costs
GDP growth measures output but does not account for environmental degradation or resource depletion. As a result, economies may appear to be growing even as they harm the environment.
2. Fails to Reflect Income Inequality
GDP growth measures overall output but says little about how wealth is distributed. High growth rates can coincide with widening income gaps.
3. Excludes Non-Market Activities
Many valuable activities, such as unpaid household work and volunteer efforts, are excluded from GDP calculations, leading to an incomplete picture of economic activity.
Conclusion: The Role of GDP Growth in Economic Analysis
In summary, GDP growth is a vital economic indicator that provides insight into a nation’s economic performance and prospects. While it plays a crucial role in guiding policy and investment decisions, it is not without limitations. To fully understand economic well-being, GDP growth should be considered alongside other metrics, such as employment, inflation, and environmental sustainability.
Whether you are a policymaker, business leader, or investor, keeping an eye on GDP growth and understanding its nuances can help you navigate the complexities of the modern economy with greater confidence.
For You
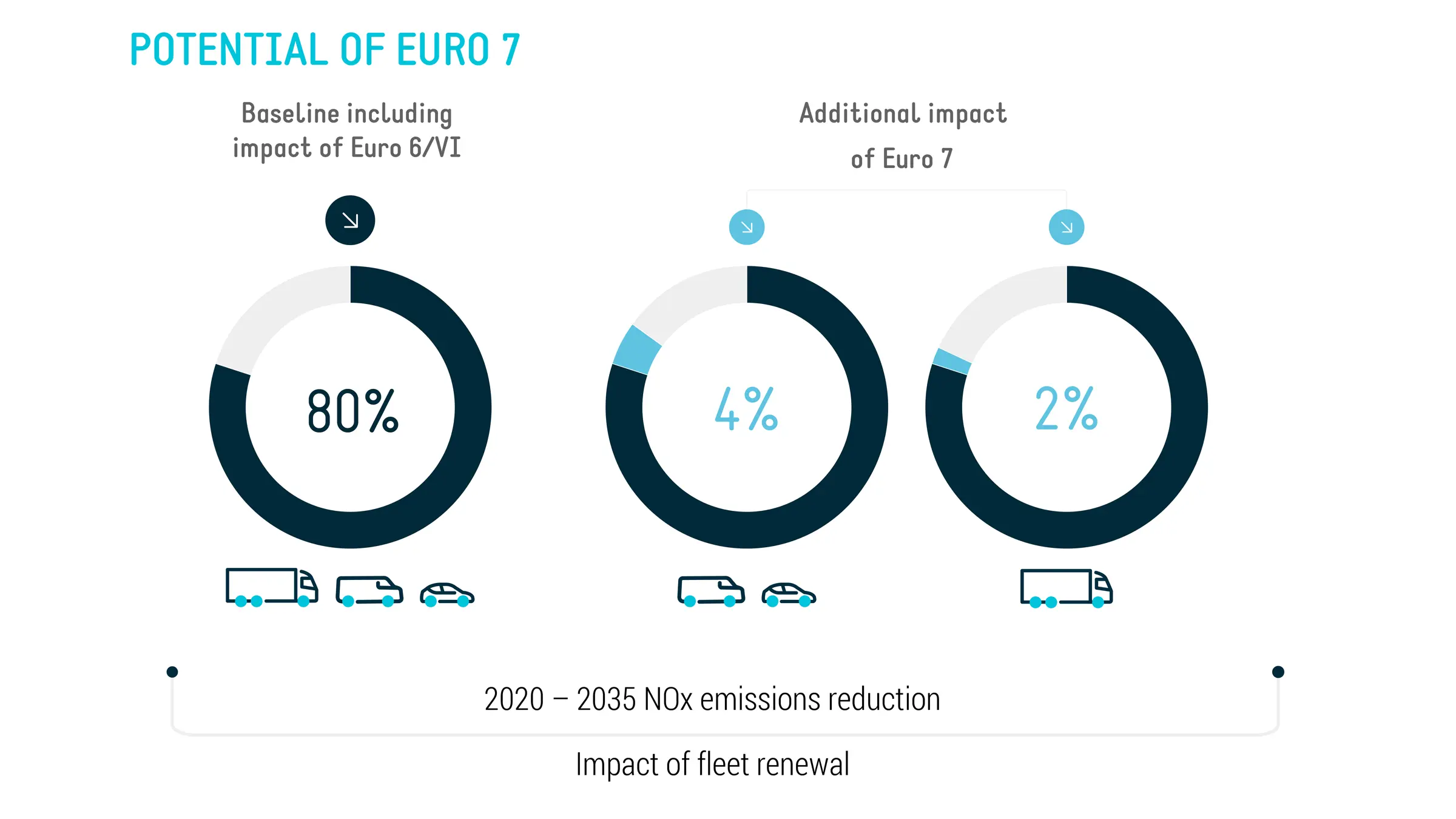
View AllUnderstand Euro 6 emission standards and their impact on car manufacturing and air quality. Stay informed on environmental policy!
Mia Wilson
Learn how blockchain is powering the NFT market and what it means for creators.
Mia Wilson
Learn how VPS hosting boosts website performance and speeds up loading times.
Mia Wilson
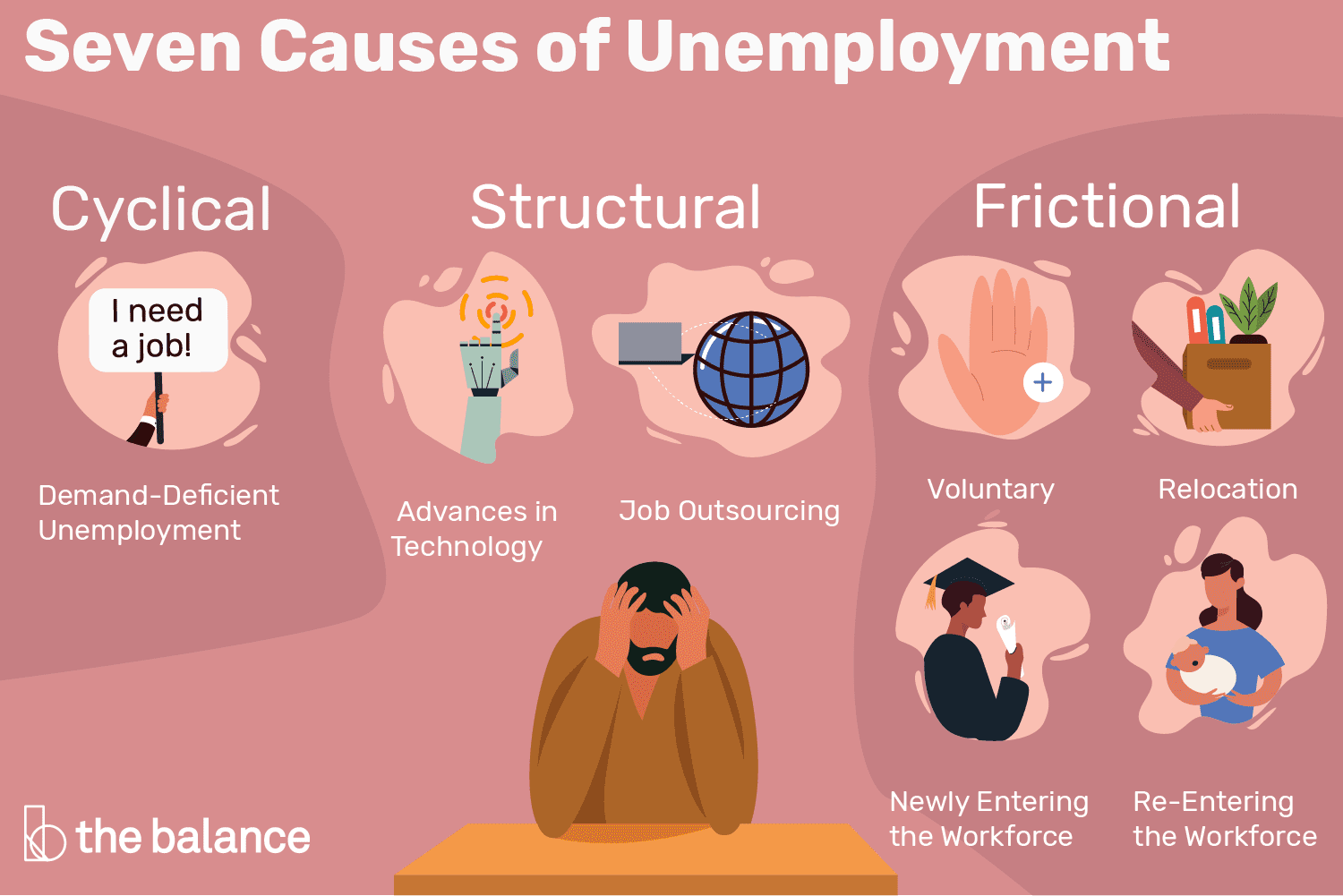
Dive into the main causes of unemployment and how they affect the economy. Learn more about this critical issue!
Mia Wilson
Get insights into VPS hosting prices and how to choose an affordable plan.
Mia Wilson
Explore various economic forecasting methods and their importance in decision-making. Click to gain clear insights!
Mia Wilson
Education
View All
April 24, 2025
What Is Distance Education? Explained!
Discover how distance education works, its benefits, and how it’s transforming learning. Start your journey today!
April 17, 2025
What Is Secondary Education? Explained!
Learn about secondary education, its structure, and its role in shaping academic and career paths. Get insights today!

April 16, 2025
Why Is Education Important?
Explore why education is vital for personal growth, career success, and societal progress. Start learning now!