Antitrust Laws Explained: A Quick Guide
Mia Wilson

Photo: Antitrust Laws Explained: A Quick Guide
Antitrust Laws Explained: A Quick Guide
Antitrust laws play a critical role in maintaining a competitive marketplace by preventing unfair business practices that stifle competition. These regulations are essential for ensuring consumers benefit from fair prices, high-quality products, and innovation. Understanding the basics of antitrust laws can help individuals and businesses navigate legal landscapes while promoting healthy competition.
What Are Antitrust Laws?
Antitrust laws are regulations established by governments to prevent monopolistic practices, promote competition, and ensure a level playing field in the marketplace. These laws target practices such as price-fixing, collusion, and mergers that could lead to unfair dominance by a single entity.
In the United States, antitrust laws date back to the late 19th century, with notable legislation including:
- The Sherman Antitrust Act (1890): The first federal law aimed at prohibiting monopolies and any agreements that restrict trade.
- The Clayton Act (1914): This law addressed specific practices not clearly covered by the Sherman Act, such as mergers and acquisitions that reduce competition.
- The Federal Trade Commission Act (1914): This act established the Federal Trade Commission (FTC), which enforces antitrust laws and promotes consumer protection.
Why Are Antitrust Laws Important?
Antitrust laws serve several vital purposes:
- Promoting Competition: By curbing monopolistic behavior, these laws ensure multiple businesses can compete in a market, leading to better products and services.
- Protecting Consumers: Competitive markets result in fair pricing, more choices, and innovation, all of which benefit consumers.
- Preventing Economic Concentration: These regulations prevent excessive concentration of market power in the hands of a few corporations, safeguarding smaller businesses.
Key Principles of Antitrust Laws
1. Prohibition of Monopolization
A monopoly occurs when a single company dominates a market without viable competitors. While being a monopoly isn’t illegal by itself, using anti-competitive practices to maintain or establish a monopoly is prohibited. Examples include:
- Predatory Pricing: Selling products below cost to drive out competitors.
- Exclusive Contracts: Forcing suppliers or customers to deal only with one company.
2. Prevention of Collusion and Cartels
Collusion occurs when businesses conspire to set prices or divide markets, harming consumers by reducing competition. Cartels, which are formal agreements between firms to control prices or production, are illegal under antitrust laws.
Examples include:
- Price-Fixing Agreements: Competitors agreeing to set similar prices.
- Market Division: Companies agreeing to split up territories to avoid competition.
3. Regulation of Mergers and Acquisitions
Mergers and acquisitions can lead to reduced competition, especially when large firms acquire smaller competitors. Antitrust authorities closely scrutinize these deals to prevent the formation of monopolies or dominant market players.
The FTC and the Department of Justice (DOJ) review proposed mergers to assess their impact on competition. If a merger is likely to harm consumers, it may be blocked or require modifications.
How Antitrust Laws Are Enforced
1. Government Enforcement
Government agencies, primarily the FTC and the DOJ in the United States, play a leading role in enforcing antitrust laws. They investigate potential violations, bring lawsuits against offenders, and ensure compliance with regulations.
2. Private Lawsuits
In addition to government action, private parties harmed by anti-competitive practices can file lawsuits. Successful plaintiffs may recover triple the damages they incurred, a provision designed to deter violations and encourage compliance.
3. International Cooperation
Given the global nature of modern business, international cooperation is crucial in enforcing antitrust laws. Countries often work together to investigate cross-border violations and ensure multinational corporations adhere to competition rules.
Notable Antitrust Cases
Several high-profile antitrust cases have shaped the enforcement and interpretation of these laws:
- United States v. Microsoft Corp. (1998): The DOJ sued Microsoft for abusing its monopoly power in the PC operating systems market. The case resulted in significant changes to Microsoft’s business practices.
- AT&T Breakup (1982): The U.S. government forced the breakup of AT&T, which had a monopoly on telephone services, into smaller regional companies.
- EU vs. Google (2017): The European Union fined Google for anti-competitive practices related to its search engine dominance.
Criticisms and Challenges of Antitrust Laws
While antitrust laws are vital for promoting competition, they are not without criticism:
- Ambiguity: The broad language in antitrust statutes can lead to differing interpretations and uncertainty for businesses.
- Enforcement Complexity: Investigating and prosecuting violations can be time-consuming and costly.
- Balancing Innovation: Some argue that stringent antitrust enforcement can stifle innovation, especially in fast-moving tech industries.
Despite these challenges, most experts agree that antitrust laws are essential for maintaining a fair and competitive economy.
The Future of Antitrust Regulation
As markets evolve, especially with the rise of digital platforms and tech giants, antitrust regulation faces new challenges. Issues such as data dominance, network effects, and platform neutrality are now at the forefront of antitrust debates.
Potential future developments include:
- Stronger Regulation of Digital Markets: Governments may introduce new rules targeting the unique dynamics of digital platforms.
- Increased Global Cooperation: With multinational corporations operating across borders, greater international collaboration is likely.
- Enhanced Consumer Protections: Policymakers may focus more on protecting consumer data and privacy in the context of competition.
Conclusion
Antitrust laws are fundamental for fostering competition, protecting consumers, and preventing market abuses. While enforcement can be complex and controversial, the overarching goal remains clear: to promote a vibrant, competitive economy where businesses can thrive, innovate, and serve consumers fairly. As markets continue to evolve, so too must antitrust policies, ensuring they remain effective in a rapidly changing world.
For You
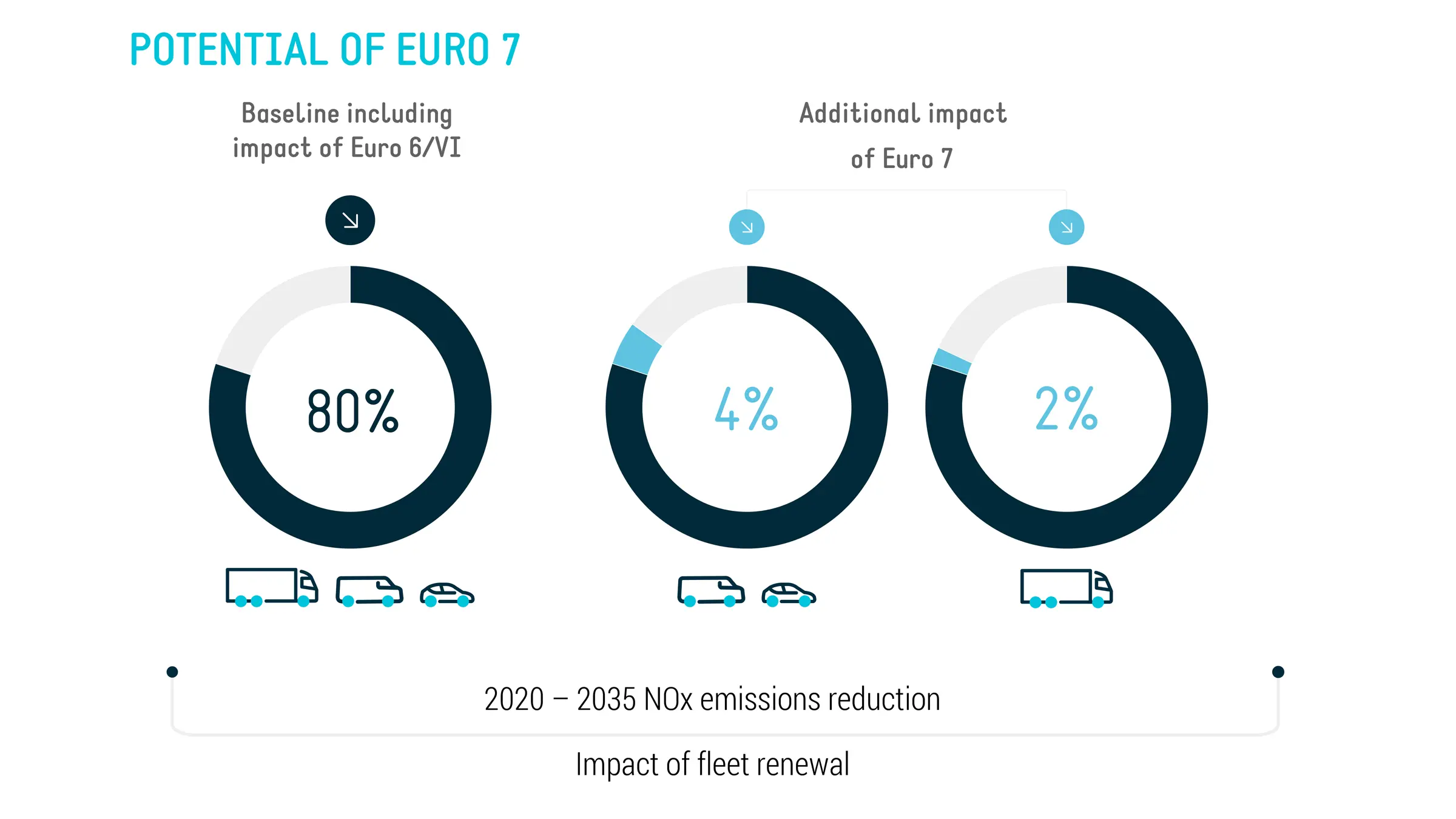
View AllUnderstand Euro 6 emission standards and their impact on car manufacturing and air quality. Stay informed on environmental policy!
Mia Wilson
Learn how blockchain is powering the NFT market and what it means for creators.
Mia Wilson
Learn how VPS hosting boosts website performance and speeds up loading times.
Mia Wilson
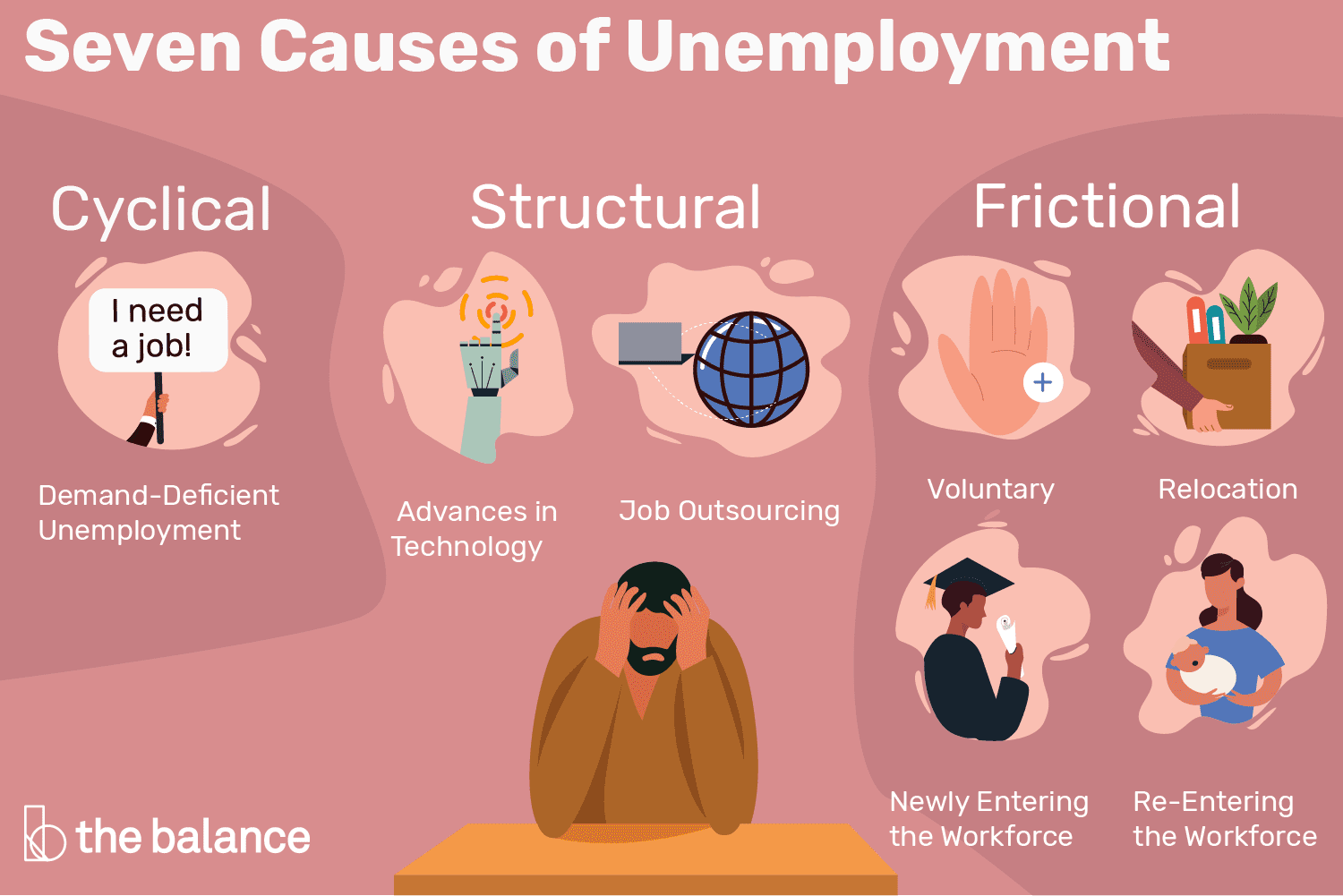
Dive into the main causes of unemployment and how they affect the economy. Learn more about this critical issue!
Mia Wilson
Get insights into VPS hosting prices and how to choose an affordable plan.
Mia Wilson
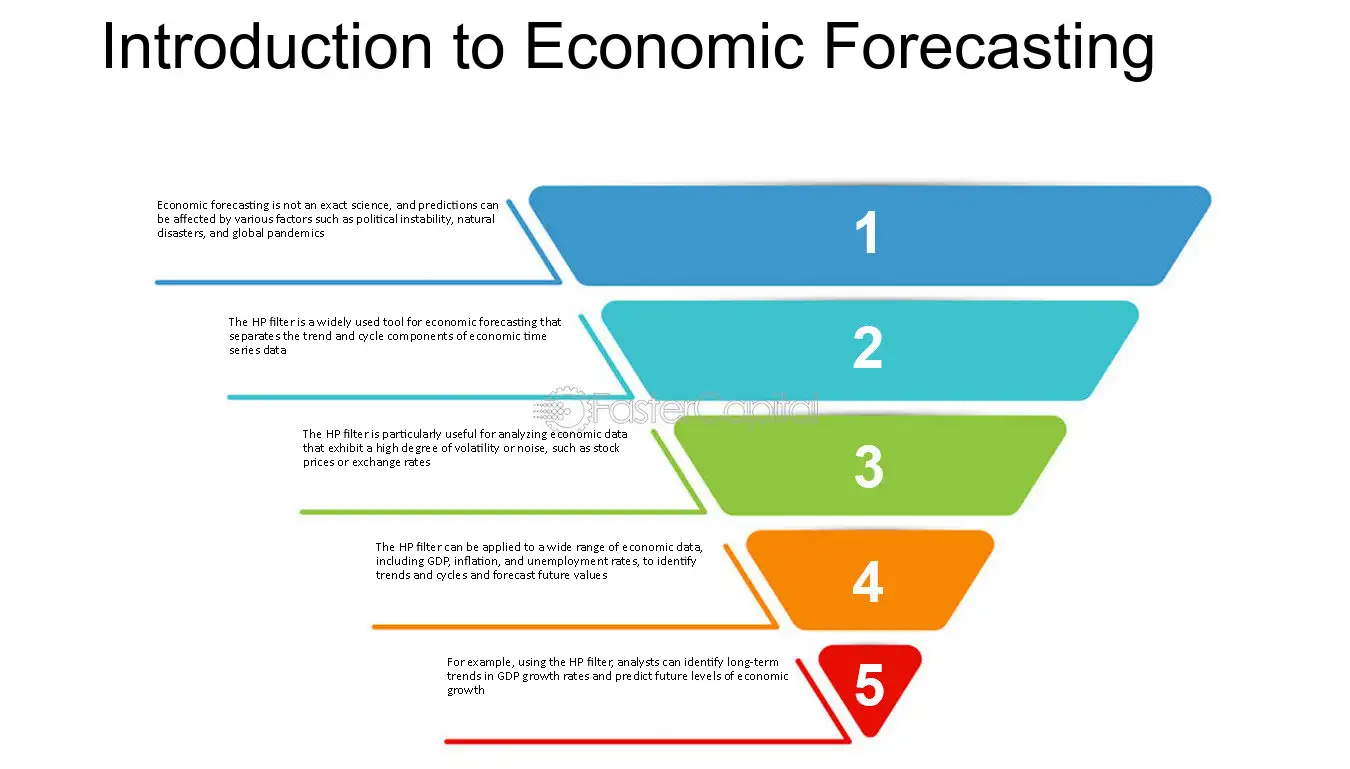
Explore various economic forecasting methods and their importance in decision-making. Click to gain clear insights!
Mia Wilson
Education
View All
April 24, 2025
What Is Distance Education? Explained!
Discover how distance education works, its benefits, and how it’s transforming learning. Start your journey today!
April 17, 2025
What Is Secondary Education? Explained!
Learn about secondary education, its structure, and its role in shaping academic and career paths. Get insights today!

April 16, 2025
Why Is Education Important?
Explore why education is vital for personal growth, career success, and societal progress. Start learning now!