Behavioral Economics Basics Explained
Mia Wilson

Photo: Behavioral Economics Basics Explained
Behavioral Economics Basics Explained: Understanding Human Decision-Making
Behavioral economics is a fascinating field that blends psychology with economics to explore how individuals make decisions. Unlike traditional economics, which assumes people act rationally to maximize their self-interest, behavioral economics acknowledges that human behavior often deviates from rationality. By understanding these deviations, businesses, policymakers, and individuals can make better decisions and design systems that align with real human behavior. In this article, we’ll explain the basics of behavioral economics, its key principles, and its practical applications.
What is Behavioral Economics?
Behavioral economics is a subfield of economics that studies how psychological, social, and emotional factors affect economic decisions. Traditional economic theories assume that people are rational actors who always make decisions in their best interest. However, in real life, people are influenced by biases, heuristics, and emotions, which often lead to irrational decisions. Behavioral economics seeks to explain why this happens and how it can be predicted.
For example, when faced with a choice between saving money for the future and spending on a luxury item today, many people choose the latter, even though saving might be more beneficial in the long run. This behavior can be explained by the concept of present bias, a key principle in behavioral economics that highlights people’s tendency to prioritize immediate gratification over long-term benefits.
Key Principles of Behavioral Economics
1. Bounded Rationality
Herbert Simon, a pioneer in the field, introduced the concept of bounded rationality, which suggests that human decision-making is limited by available information, cognitive limitations, and time constraints. Unlike the idealized "rational actor" in classical economics, real people operate with incomplete knowledge and limited processing abilities.
2. Heuristics and Biases
People often use mental shortcuts, known as heuristics, to make decisions quickly. While these shortcuts can be helpful, they also lead to predictable errors or biases. Daniel Kahneman and Amos Tversky, two prominent figures in behavioral economics, identified several key biases, including:
- Anchoring Bias: Relying too heavily on the first piece of information encountered.
- Availability Heuristic: Judging the likelihood of events based on how easily examples come to mind.
- Loss Aversion: The tendency to prefer avoiding losses over acquiring equivalent gains, meaning that losing $10 feels worse than gaining $10 feels good.
3. Prospect Theory
Developed by Kahneman and Tversky, prospect theory describes how people perceive gains and losses. Unlike traditional utility theory, which assumes a consistent approach to risk, prospect theory shows that people are risk-averse when it comes to gains but risk-seeking when facing potential losses. This helps explain behaviors such as gambling and insurance purchases.
4. Nudge Theory
Popularized by Richard Thaler, nudge theory involves subtly guiding people’s behavior through changes in the way choices are presented. Nudges don’t restrict options instead, they make the desired option more accessible or appealing. Examples include automatically enrolling employees in retirement savings plans or placing healthier foods at eye level in supermarkets to encourage better dietary choices.
Applications of Behavioral Economics
1. Marketing and Consumer Behavior
Businesses use insights from behavioral economics to influence consumer behavior. Techniques such as framing, anchoring, and scarcity marketing are common. For instance, highlighting that a discount is "only available for a limited time" leverages scarcity to drive immediate action. Similarly, framing a product as "95% fat-free" rather than "contains 5% fat" can significantly impact consumer perception.
2. Public Policy and Social Programs
Governments apply behavioral economics to design policies that promote better health, financial well-being, and social outcomes. A notable example is the use of nudges to increase organ donation rates by making donation the default option unless individuals opt out. This approach has proven far more effective than requiring explicit opt-in consent.
3. Personal Finance
Behavioral economics offers valuable insights into improving personal financial decisions. Concepts like mental accounting explain why people categorize money into separate "accounts" (e.g., a vacation fund and a savings account), leading to suboptimal financial behavior. By understanding biases such as overconfidence and present bias, individuals can take steps to make better long-term financial decisions.
4. Workplace Productivity
Employers can apply behavioral economics to enhance employee engagement and productivity. Offering small, immediate rewards for task completion leverages present bias to motivate workers, while structuring tasks to reduce decision fatigue can improve overall performance.
Criticism and Limitations of Behavioral Economics
Despite its growing popularity, behavioral economics is not without criticism. One major concern is its reliance on experimental studies conducted in controlled environments, which may not always translate to real-world settings. Additionally, some critics argue that nudging can be manipulative, raising ethical questions about autonomy and consent.
Moreover, while behavioral economics provides insights into irrational behavior, it doesn’t always offer clear solutions. Human behavior is complex, and what works in one context may fail in another. Therefore, while behavioral economics is a powerful tool, it should be applied thoughtfully, considering cultural and contextual differences.
Conclusion
Behavioral economics bridges the gap between psychology and traditional economics, offering a more realistic view of how people make decisions. By acknowledging human limitations and biases, it helps explain behaviors that standard economic models cannot. Whether it’s improving personal finances, designing better public policies, or creating more effective marketing strategies, the principles of behavioral economics have far-reaching applications.
Understanding the basics of behavioral economics empowers individuals and organizations to make more informed choices and design environments that promote better outcomes. As research in this field continues to evolve, its influence on economics, policy, and everyday life is likely to grow, offering new insights into the complexities of human behavior.
For You
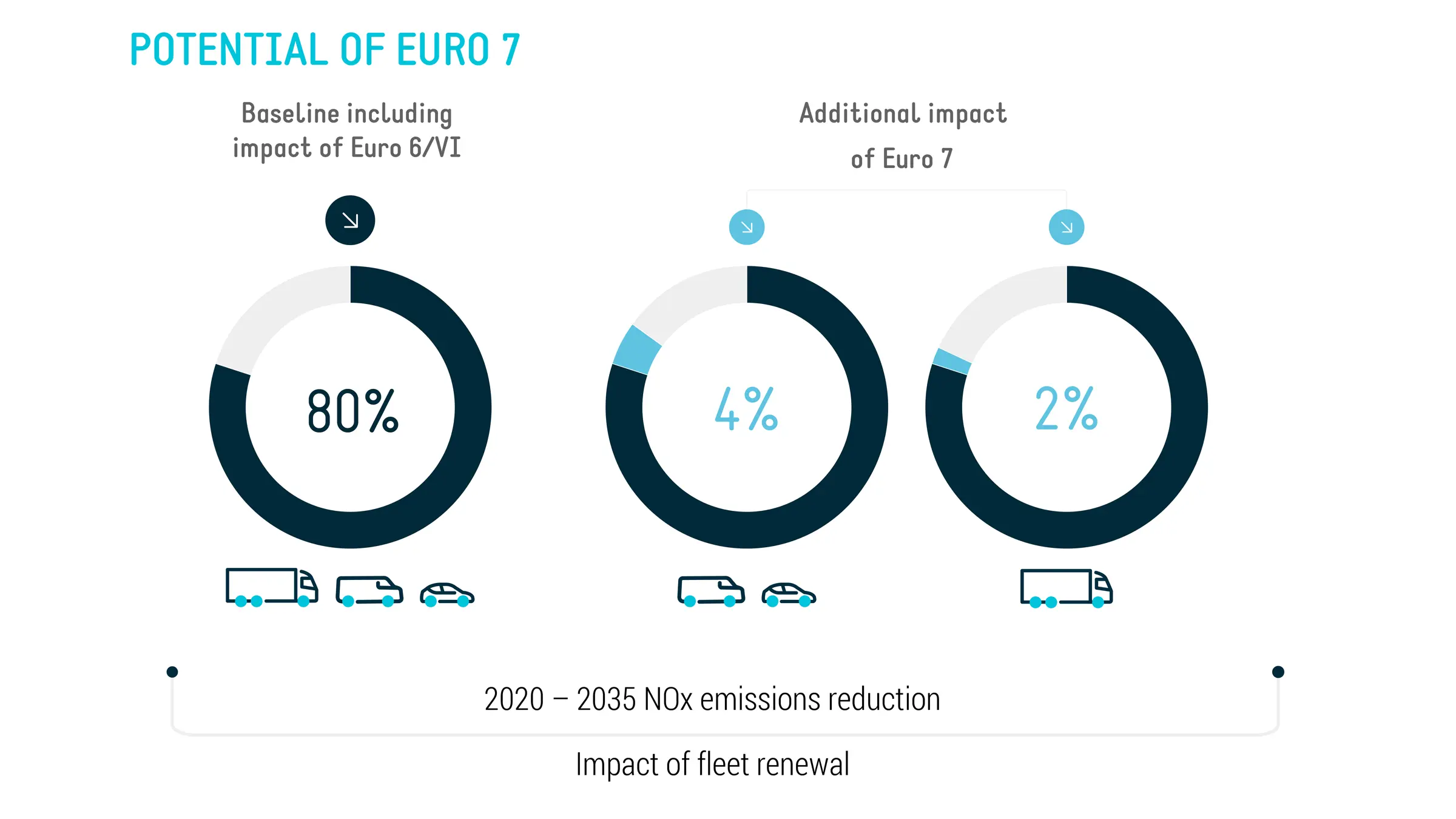
View AllUnderstand Euro 6 emission standards and their impact on car manufacturing and air quality. Stay informed on environmental policy!
Mia Wilson
Learn how blockchain is powering the NFT market and what it means for creators.
Mia Wilson
Learn how VPS hosting boosts website performance and speeds up loading times.
Mia Wilson
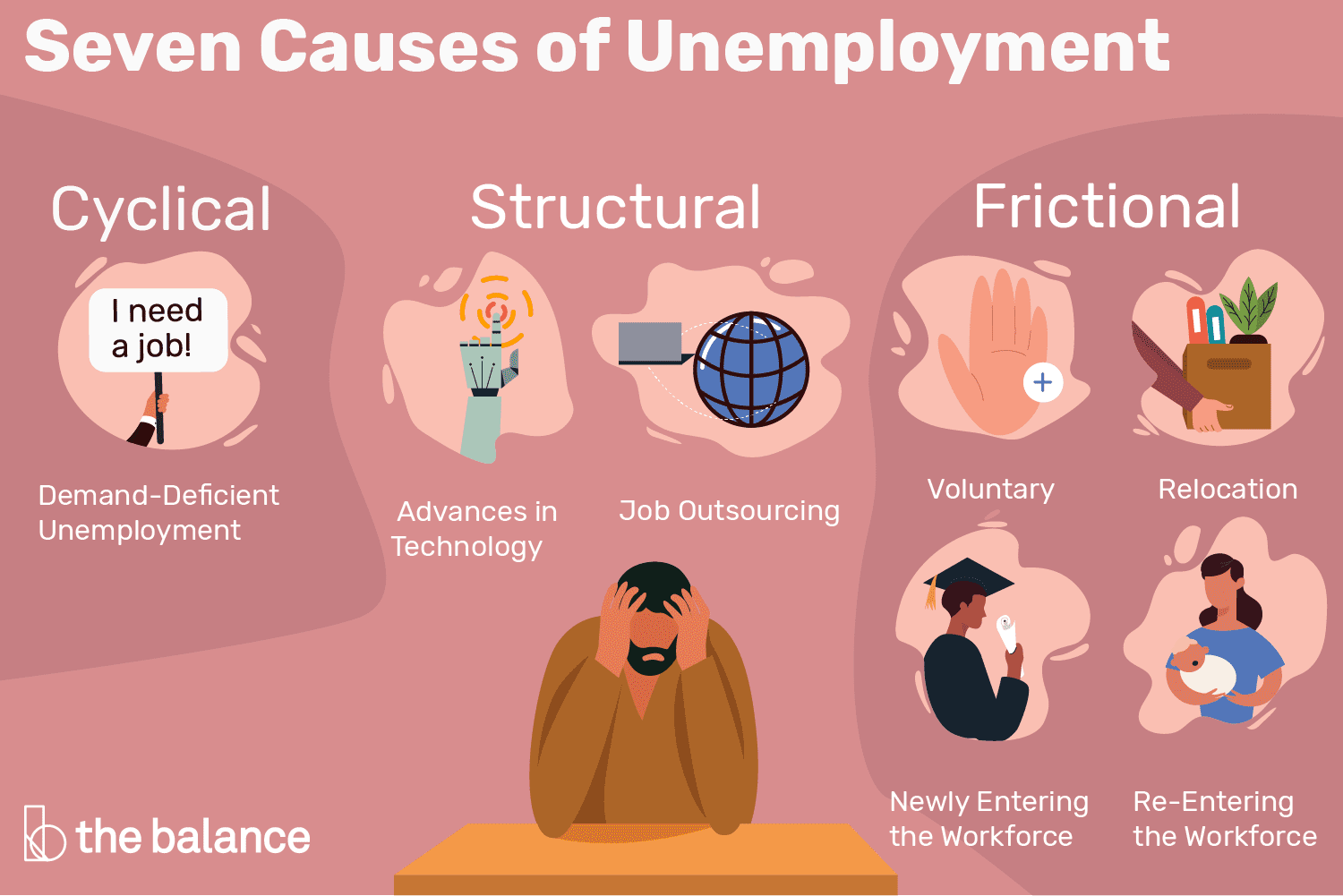
Dive into the main causes of unemployment and how they affect the economy. Learn more about this critical issue!
Mia Wilson
Get insights into VPS hosting prices and how to choose an affordable plan.
Mia Wilson
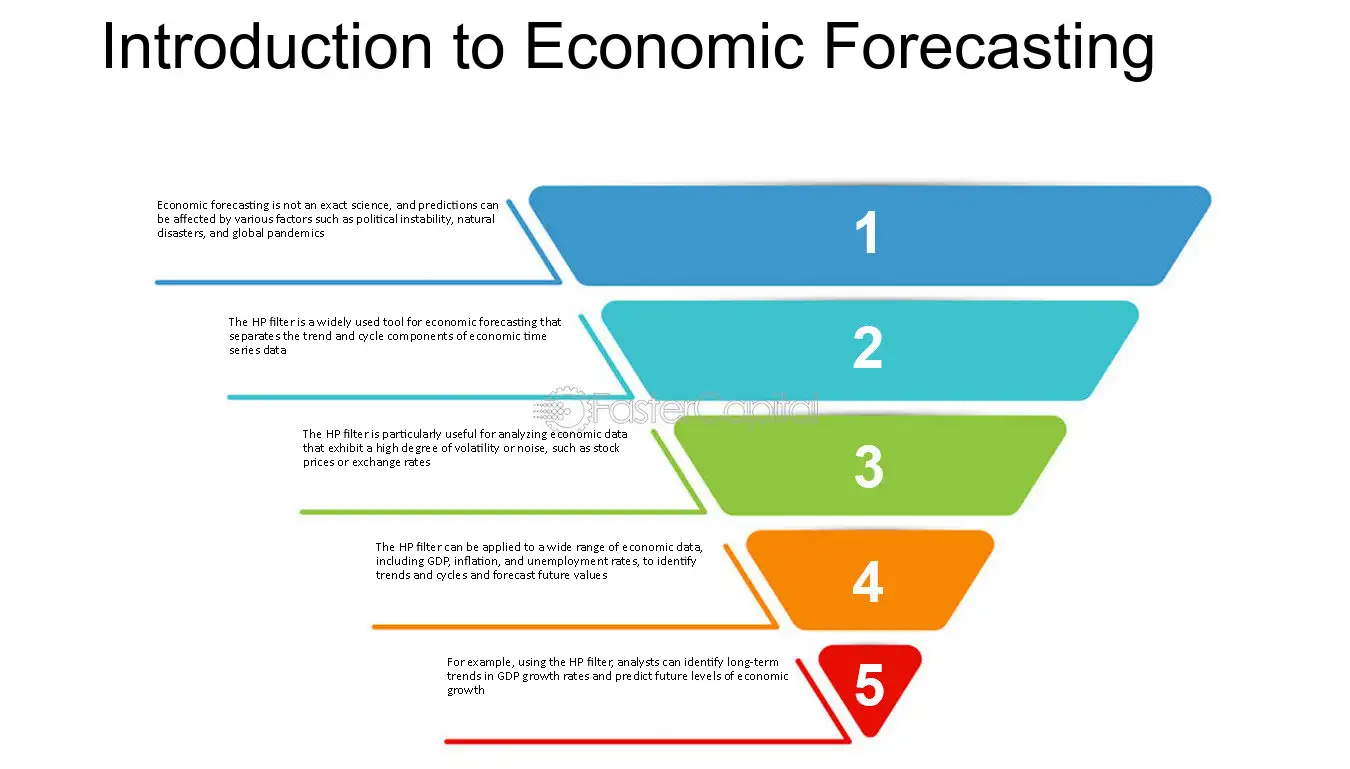
Explore various economic forecasting methods and their importance in decision-making. Click to gain clear insights!
Mia Wilson
Education
View All
April 24, 2025
What Is Distance Education? Explained!
Discover how distance education works, its benefits, and how it’s transforming learning. Start your journey today!
April 17, 2025
What Is Secondary Education? Explained!
Learn about secondary education, its structure, and its role in shaping academic and career paths. Get insights today!

April 16, 2025
Why Is Education Important?
Explore why education is vital for personal growth, career success, and societal progress. Start learning now!