What Are Macroeconomic Indicators?
Mia Wilson
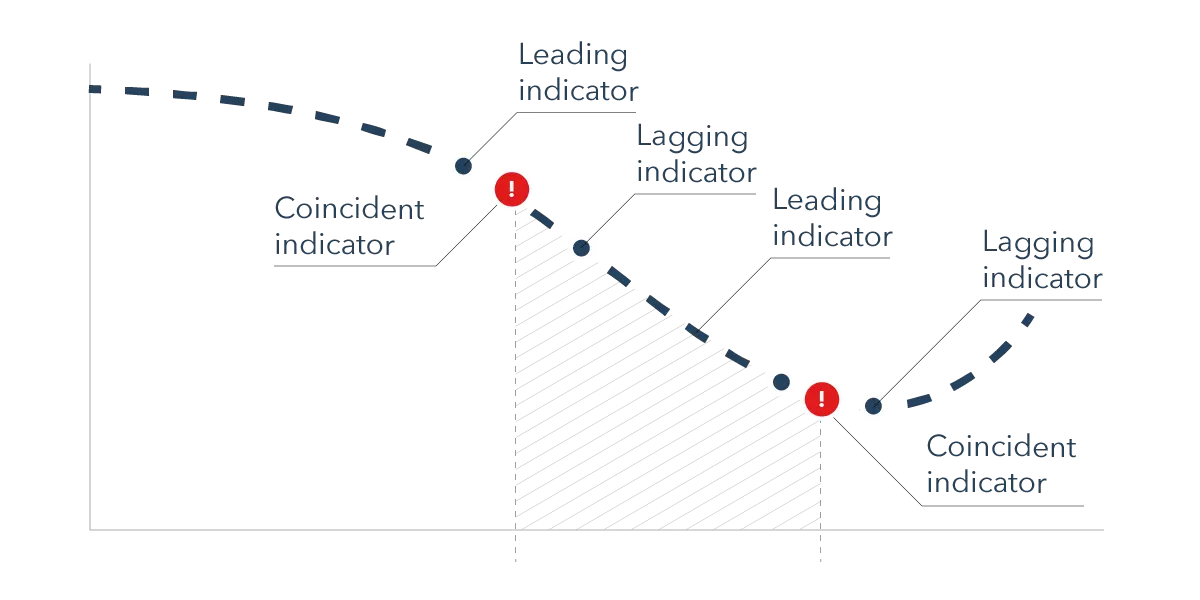
Photo: What Are Macroeconomic Indicators?
What Are Macroeconomic Indicators? A Comprehensive Guide
Macroeconomic indicators are key statistics that reflect the overall health, performance, and trends of an economy. They provide valuable insights for policymakers, investors, businesses, and analysts, helping them make informed decisions. Understanding these indicators is crucial for anyone looking to interpret economic trends or predict potential market shifts.
This article will explore the fundamental macroeconomic indicators, their significance, and how they influence decision-making in various sectors.
Introduction to Macroeconomic Indicators
A macroeconomic indicator is a quantifiable metric that represents economic activity or performance on a broad scale. Governments, financial institutions, and market participants use these indicators to assess whether an economy is growing, stagnating, or declining.
These indicators can be divided into leading, lagging, and coincident indicators:
- Leading indicators predict future economic trends.
- Lagging indicators confirm trends after they have occurred.
- Coincident indicators move in tandem with the economy, reflecting its current state.
By closely monitoring macroeconomic indicators, stakeholders can anticipate changes in economic conditions and adjust their strategies accordingly.
Key Types of Macroeconomic Indicators
1. Gross Domestic Product (GDP)
Gross Domestic Product (GDP) is perhaps the most commonly referenced macroeconomic indicator. It represents the total market value of all finished goods and services produced within a country during a specific period.
Why GDP Matters
- Economic growth: A rising GDP indicates that an economy is expanding, which is typically associated with increased job opportunities, higher income levels, and improved living standards.
- Policy decisions: Governments and central banks often use GDP growth rates to set fiscal and monetary policies.
- Investment analysis: Investors monitor GDP trends to gauge the potential profitability of investments in specific markets.
There are three primary methods to calculate GDP:
- Production approach
- Income approach
- Expenditure approach
2. Inflation Rate
The inflation rate measures the pace at which the general price level of goods and services rises over time. Moderate inflation is considered normal in a healthy economy, but excessive inflation can erode purchasing power.
Key Measures of Inflation
- Consumer Price Index (CPI): Tracks the changes in prices of a basket of consumer goods and services.
- Producer Price Index (PPI): Measures price changes from the perspective of producers.
Implications of Inflation
- High inflation reduces the purchasing power of consumers and increases business costs.
- Deflation, on the other hand, can lead to reduced economic activity and increased unemployment.
Central banks, like the U.S. Federal Reserve, manage inflation through monetary policy, adjusting interest rates to maintain price stability.
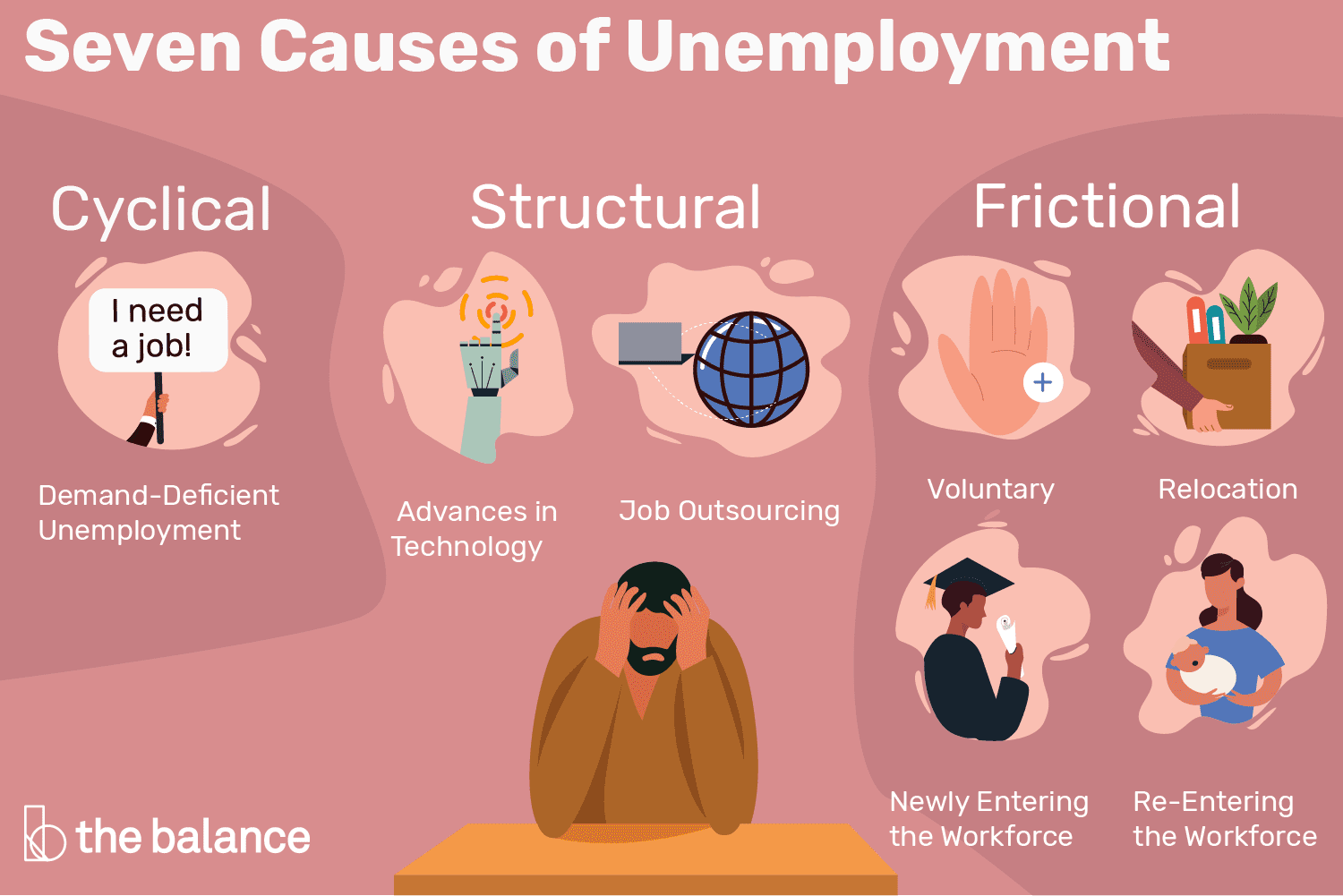
3. Unemployment Rate
The unemployment rate is a lagging indicator that reflects the percentage of the labor force that is jobless but actively seeking employment. It is a critical measure of an economy’s health, as high unemployment generally signals economic distress.
Types of Unemployment
- Frictional unemployment: Short-term joblessness as individuals transition between jobs.
- Structural unemployment: Occurs when there is a mismatch between workers’ skills and job requirements.
- Cyclical unemployment: Rises during economic downturns and falls during periods of economic growth.
A low unemployment rate is often associated with economic stability, while a high rate can indicate underlying structural issues.
4. Interest Rates
Interest rates, set by central banks, influence borrowing costs for businesses and consumers. The Federal Reserve, for example, adjusts the federal funds rate to control inflation and stimulate or cool down the economy.
How Interest Rates Affect the Economy
- Higher interest rates discourage borrowing and spending, which can slow down economic growth.
- Lower interest rates encourage borrowing, investment, and consumer spending, fostering economic expansion.
Changes in interest rates directly impact sectors such as real estate, banking, and consumer goods.
5. Balance of Trade
The balance of trade (BOT) is the difference between a country’s exports and imports. A positive balance (trade surplus) means exports exceed imports, while a negative balance (trade deficit) means the opposite.
Significance of the Balance of Trade
- A trade surplus contributes to economic growth, as it brings in more revenue from foreign markets.
- A trade deficit, while not inherently bad, can signal underlying issues like high consumer debt or lack of domestic competitiveness.
6. Consumer Confidence Index (CCI)
The Consumer Confidence Index (CCI) measures the level of optimism that consumers feel about the overall state of the economy and their personal financial situation.
Why Consumer Confidence Matters
- High consumer confidence typically leads to increased spending, which drives economic growth.
- Low confidence can result in reduced spending, slowing down economic activity.
Why Macroeconomic Indicators Are Important
Understanding macroeconomic indicators is essential for various reasons:
- Policy formulation: Governments and central banks rely on these indicators to craft effective policies.
- Investment strategy: Investors analyze indicators to assess market conditions and identify profitable opportunities.
- Business planning: Companies use economic data to forecast demand, plan production, and manage risks.
- Personal finance: Individuals can make informed decisions about saving, investing, and spending by understanding economic trends.
Challenges in Interpreting Macroeconomic Indicators
While macroeconomic indicators provide valuable information, interpreting them accurately can be challenging due to:
- Data revisions: Initial reports are often revised, which can alter the initial interpretation.
- Lag effects: Some indicators, such as unemployment, may reflect past rather than current conditions.
- Context dependency: The impact of an indicator can vary depending on the broader economic context.
For example, a rising inflation rate may be a sign of a booming economy or a symptom of supply chain disruptions.
Conclusion
Macroeconomic indicators serve as a vital compass for understanding economic trends and making informed decisions. From GDP and inflation to interest rates and consumer confidence, these metrics provide a comprehensive view of an economy’s health. Whether you are a policymaker, investor, business owner, or an informed citizen, keeping an eye on macroeconomic indicators can help you navigate the complex world of economics with greater confidence.
To stay updated, consider regularly reviewing economic reports and following reliable sources like the World Bank, International Monetary Fund (IMF), and national statistics agencies. By doing so, you can better anticipate economic shifts and make proactive decisions in both professional and personal spheres.
For You
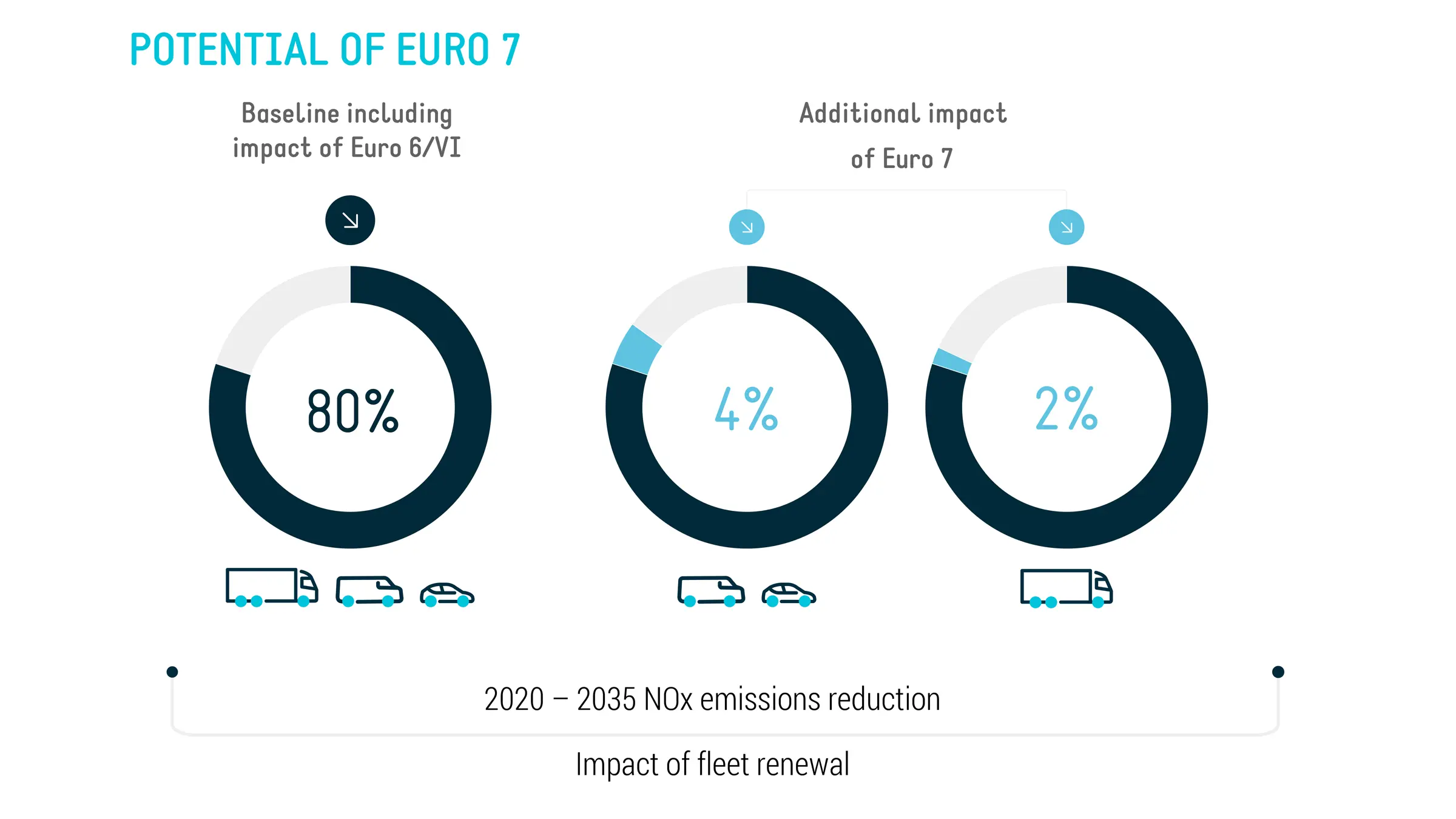
View AllUnderstand Euro 6 emission standards and their impact on car manufacturing and air quality. Stay informed on environmental policy!
Mia Wilson
Learn how blockchain is powering the NFT market and what it means for creators.
Mia Wilson
Learn how VPS hosting boosts website performance and speeds up loading times.
Mia Wilson
Dive into the main causes of unemployment and how they affect the economy. Learn more about this critical issue!
Mia Wilson
Get insights into VPS hosting prices and how to choose an affordable plan.
Mia Wilson
Explore various economic forecasting methods and their importance in decision-making. Click to gain clear insights!
Mia Wilson
Education
View All
April 24, 2025
What Is Distance Education? Explained!
Discover how distance education works, its benefits, and how it’s transforming learning. Start your journey today!
April 17, 2025
What Is Secondary Education? Explained!
Learn about secondary education, its structure, and its role in shaping academic and career paths. Get insights today!

April 16, 2025
Why Is Education Important?
Explore why education is vital for personal growth, career success, and societal progress. Start learning now!